Data Source
A data source is the entry point and foundation of AI Data, used to connect external enterprise databases or data platforms with the SERVICEME platform, enabling unified data management and analysis.
By configuring data sources, the platform can recognize external table structures, field types, and metadata information, providing support for subsequent data catalog management and business domain modeling.
Connecting Data Sources
The first step in AI Data is to connect a data source to provide foundational data for subsequent analysis.
- Supports connecting to various mainstream data platforms, including MySQL, SQL Server, Azure Databricks, etc.;
- After adding a data source, you can view all tables in this data source, and users can selectively check the tables they need to use;
- By default, the system only synchronizes metadata (such as table structure and field information), and does not synchronize actual data records, ensuring data security;
- Provides a "Test Connection" feature to ensure the connectivity of the data source is correct;
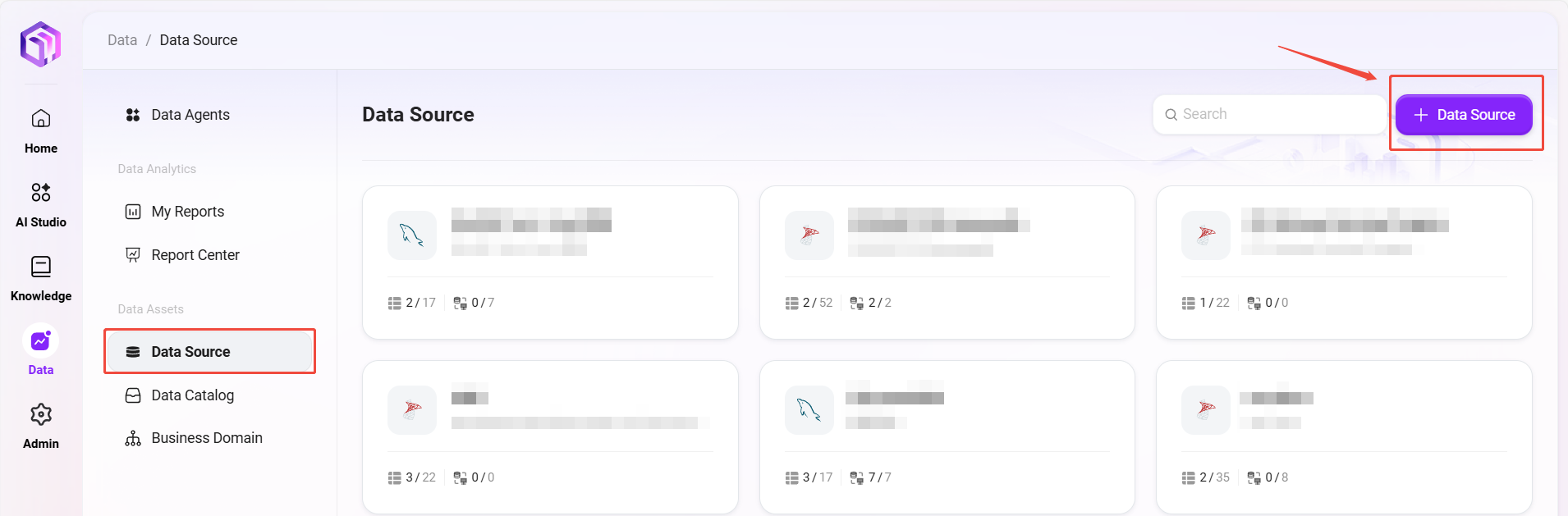
Data Source Configuration Items Description
When adding a data source, the following key information needs to be filled in:
- Data Source Type: Select the database type (such as MySQL, SQL Server, etc.);
- Connection Address: The connection string or IP of the database server;
- Database Name: The name of the target database (within 50 characters);
- Username and Password: Account information used for database authentication;
- Port Number: The port on which the database service listens;
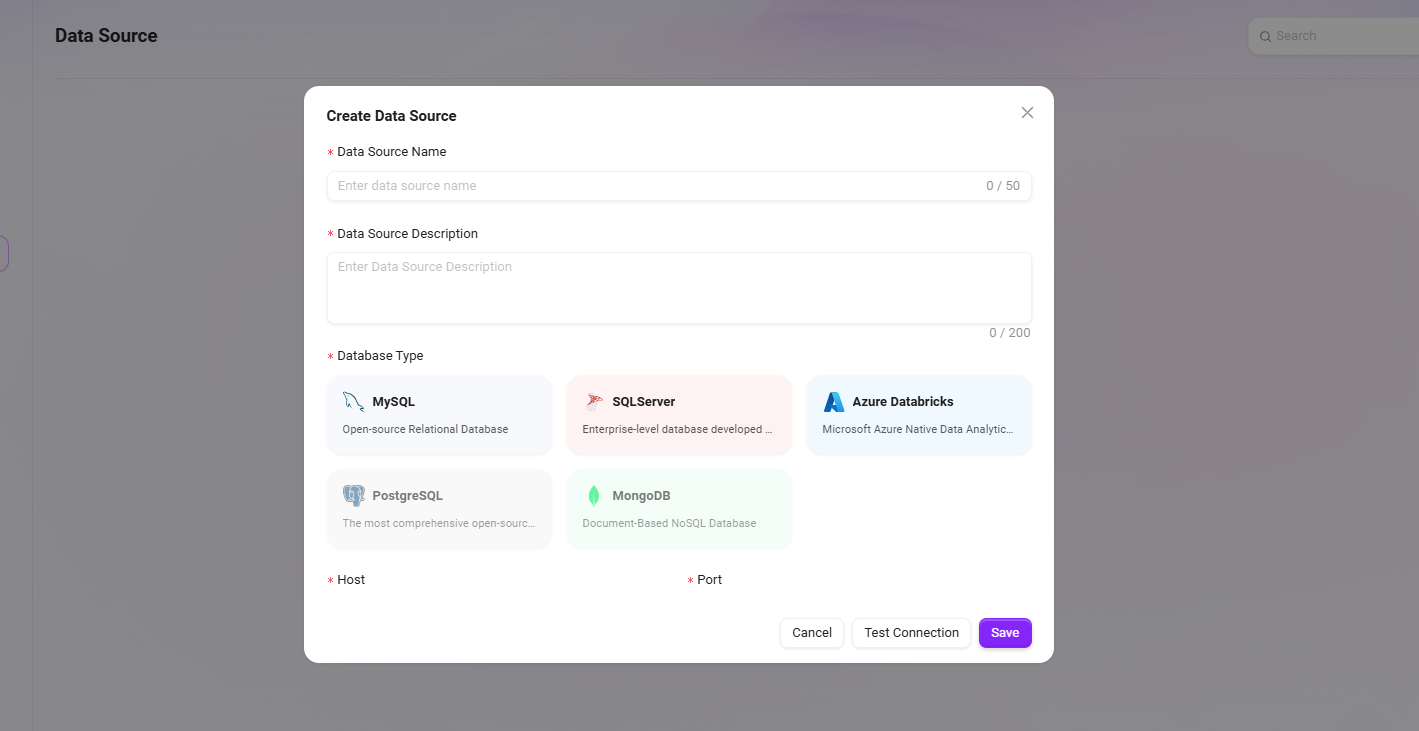
The system supports connecting to databases via the SSL protocol and can be adapted accordingly based on different database types.
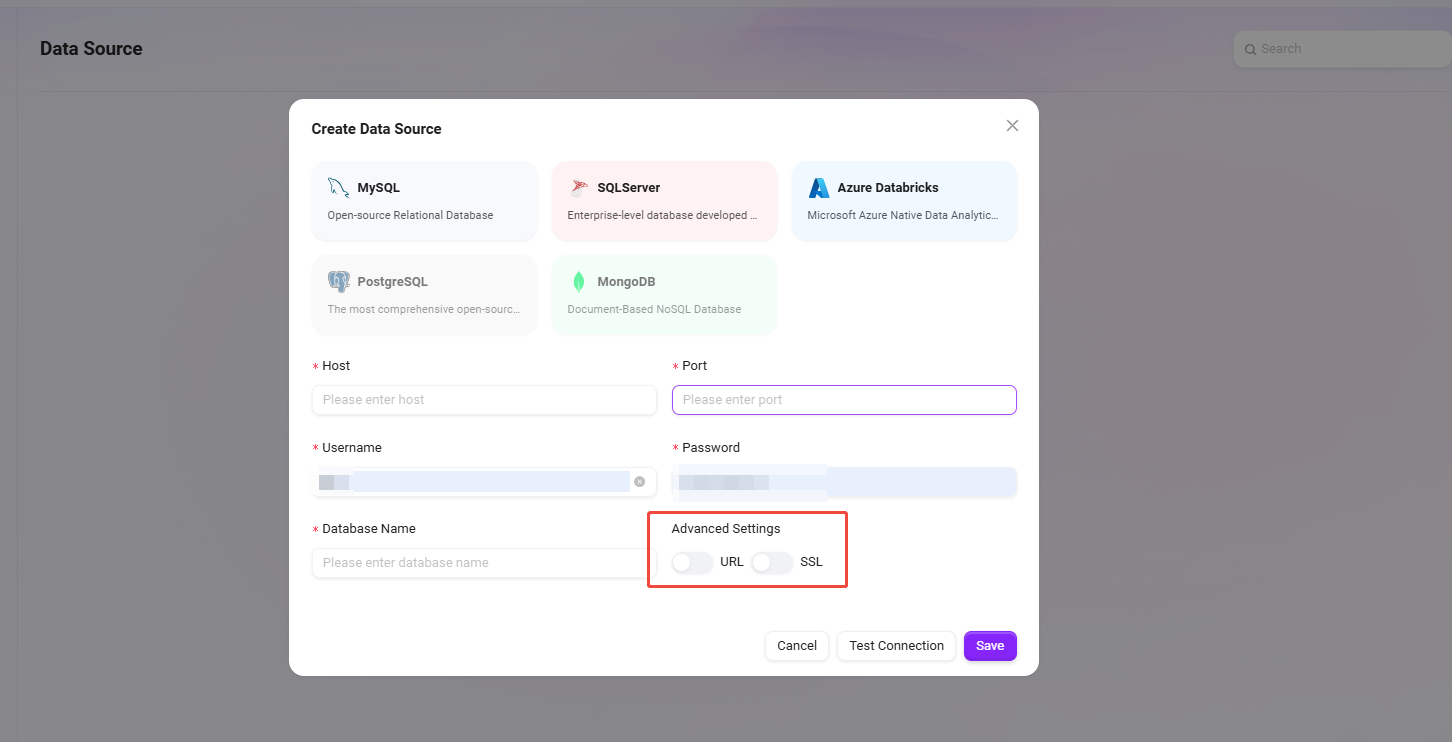
After completing the data source connection, you can add data tables.
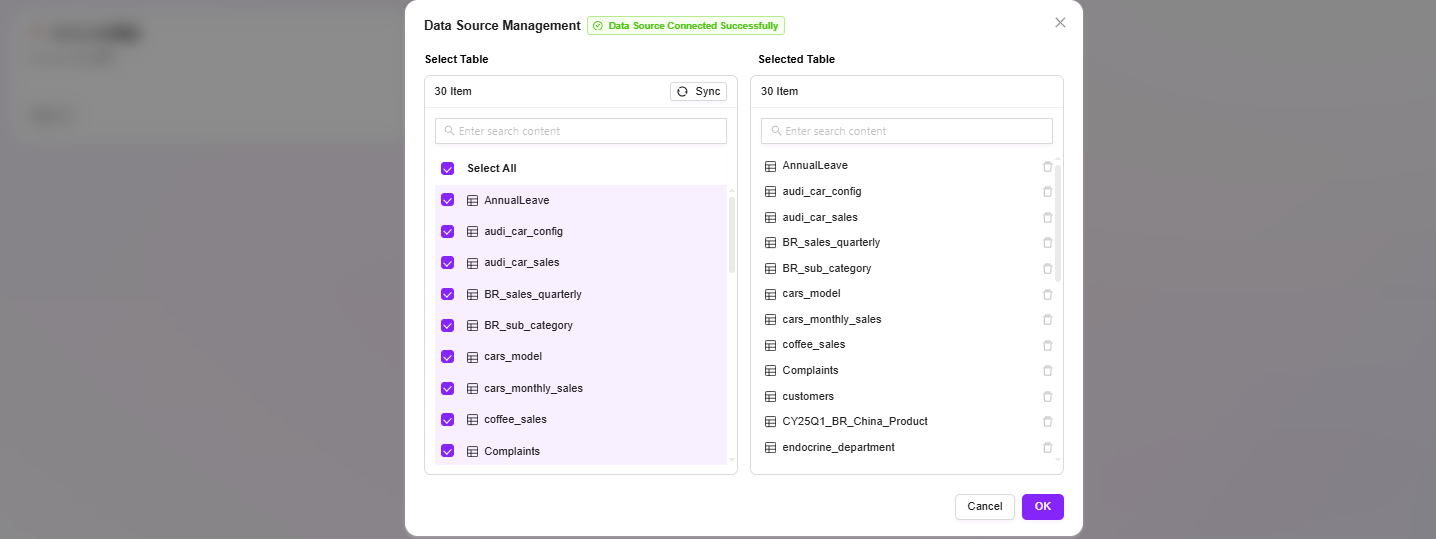
- After adding a data source, in addition to selecting data tables, you can also select views.
- Views can integrate data from multiple tables into a virtual table through query logic, suitable for displaying aggregated, filtered, or calculated results, making it easier to build more flexible data models.
- Supported database types: MySQL, SQLServer, Azure Databricks, PostgreSQL, MongDB.
Common Causes and Troubleshooting Methods for Data Source Connection Failures
When connecting to an external database, if the test connection fails, you can troubleshoot from the following aspects:
-
Incorrect Connection Information
- Check whether the hostname, port, database name, username, and password are correct.
- Confirm that the database instance allows remote access and that the firewall does not block the corresponding port (e.g., MySQL default 3306, SQL Server default 1433).
-
Special Characters Not Properly Escaped
- If the database password contains special characters (such as
@,#,%,&, etc.), note that these characters may be parsed as special symbols in the connection string, causing connection failures. - It is recommended to URL encode the password when entering it, or use contact quotes to wrap the password field in the configuration to avoid escaping issues.
- If the database password contains special characters (such as
-
Network Connectivity Issues
- Confirm that the service environment where AI Data is located can access the network where the database resides.
- If the database is in times a private network or virtual network (VNet), you need to configure the correct access policy or whitelist.
-
Insufficient Database Permissions
- Confirm that the connection account has read access to the target database and data tables.
- For cloud databases (such as Azure SQL, Databricks), also check whether the account's Token or access key is valid.
Recommendation:
If you still cannot connect after multiple tests, check the detailed error log and provide the error information to the system administrator or database administrator for further troubleshooting.