Workflow Agent Creation
Select Agent Type
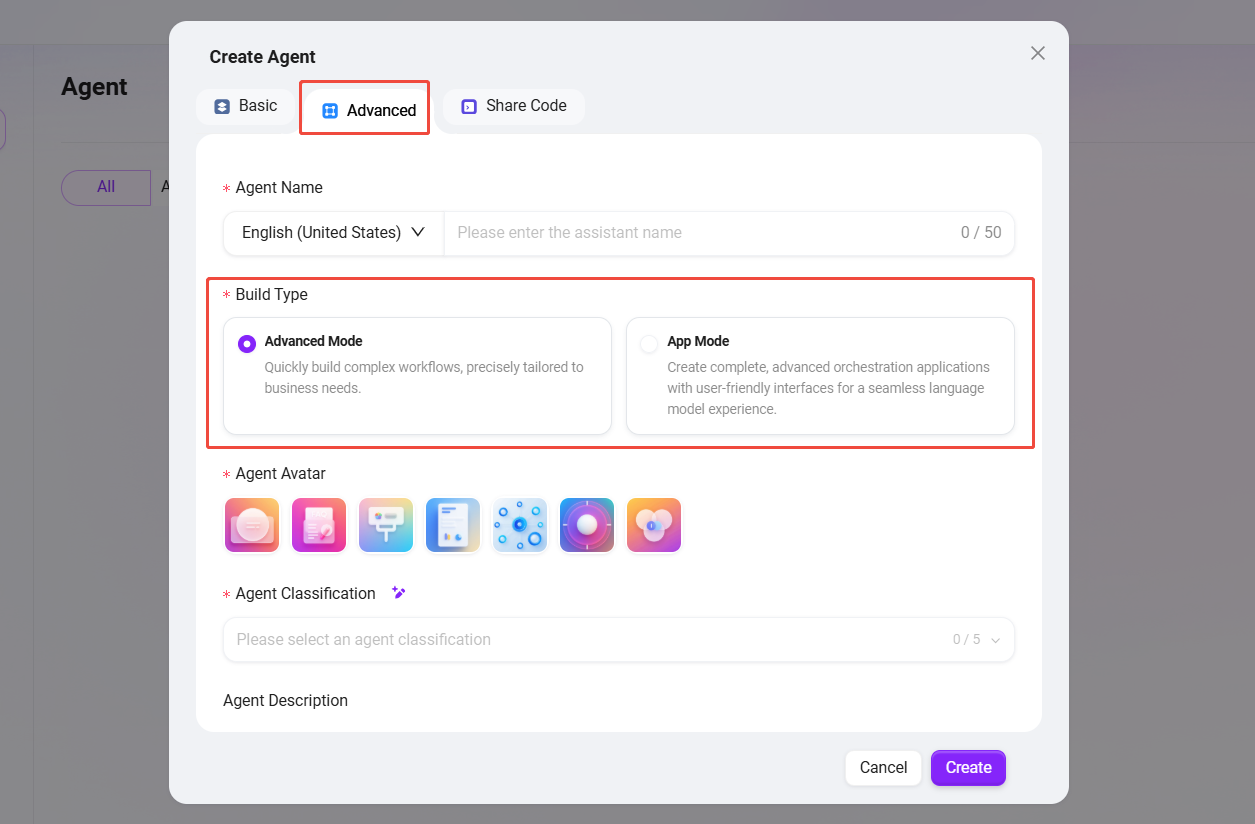
When creating an agent, select "Advanced Agent" (the initial creation steps are the same as for a regular agent).
- Build Type: Two core modes are provided to meet business needs of varying complexity.
- Advanced Mode: Quickly build complex workflows based on conversations.
- Application Mode: Create fully orchestrated applications with customized user interfaces and structured input flows, delivering a superior user experience.
Advanced Mode
An enhanced Q&A agent built on top of the basic agent, with core capabilities focused on multi-turn conversations and knowledge-based Q&A.
Features:
- Uses natural language conversation as the main interaction method.
- After creation, it will appear in the Agent List.
- Suitable for business scenarios requiring flexible, open-ended conversational interactions.
Typical Scenarios:
- Internal enterprise knowledge Q&A assistant
- Product FAQ and technical support assistant
- Ticket processing consultation assistant
Application Mode
Used to build an Agent orchestration application with UI, featuring specific input structures for completing designated tasks. It does not focus on free-form conversation, but rather on executing predefined task flows.
Features:
- After creation, it is displayed on the APP page.
- Has a fixed, customizable input interface (e.g., file upload, form field entry).
- Focuses on executing automated or semi-automated task flows.
- Supports complex input types such as files and structured data, suitable for business scenarios requiring strict input/output formats.
Typical Scenarios:
- Contract Review App (upload contract → auto-mark risks)
- Document Analysis App (upload document → auto-generate key content)
- Data Cleaning App (upload Excel → auto-process data)
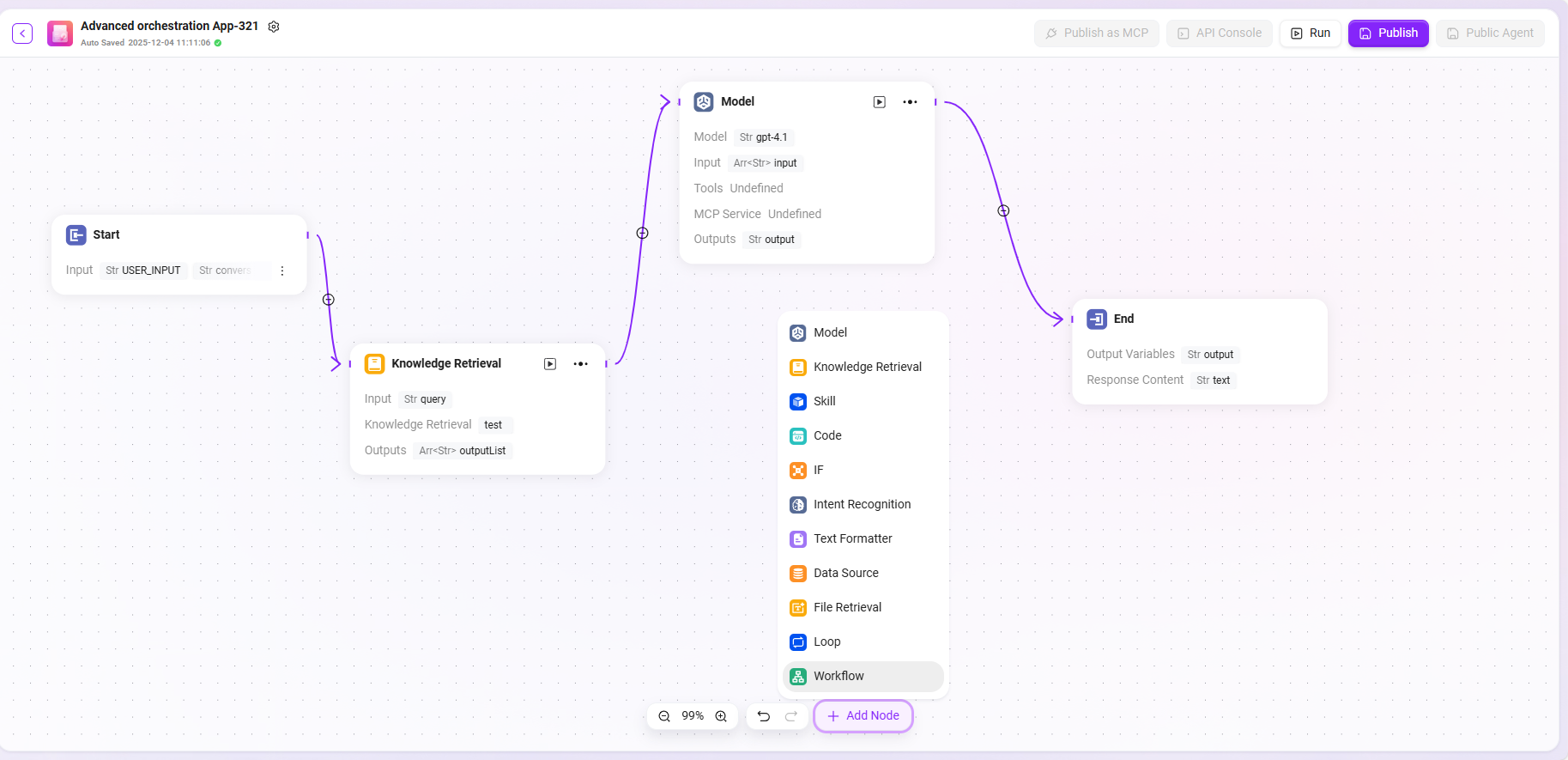
Workflow Configuration
Configure the workflow by dragging and connecting the following nodes according to the user's actual business logic:
- Start, End: Built-in input/output modules; input/output parameters and fields can be customized.
- Model: Select the model to use in this module, input variables obtained from other modules, and edit prompts and output messages, which are saved as variables.
- Knowledge Base Retrieval: Recall the most relevant information from the selected knowledge base based on input variables and return it.
- Skill: Select a skill to perform input/output actions processed by that skill.
- Code: Customize and create code functions based on output variables from other modules.
- Selector: Determine workflow branch direction based on set conditions, enabling logical judgment.
- Intent Recognition: Used for recognizing user input intent and matching it with preset intent options.
- Text Formatter: Used to process the format of multiple string-type variables.
- Data Source: Select a data source to add referenceable variable content.
- File Retrieval: Search uploaded files and find relevant answers based on input questions.
- Loop: Repeat a set of tasks for each item in a list, with optional parallel processing.
Node Details
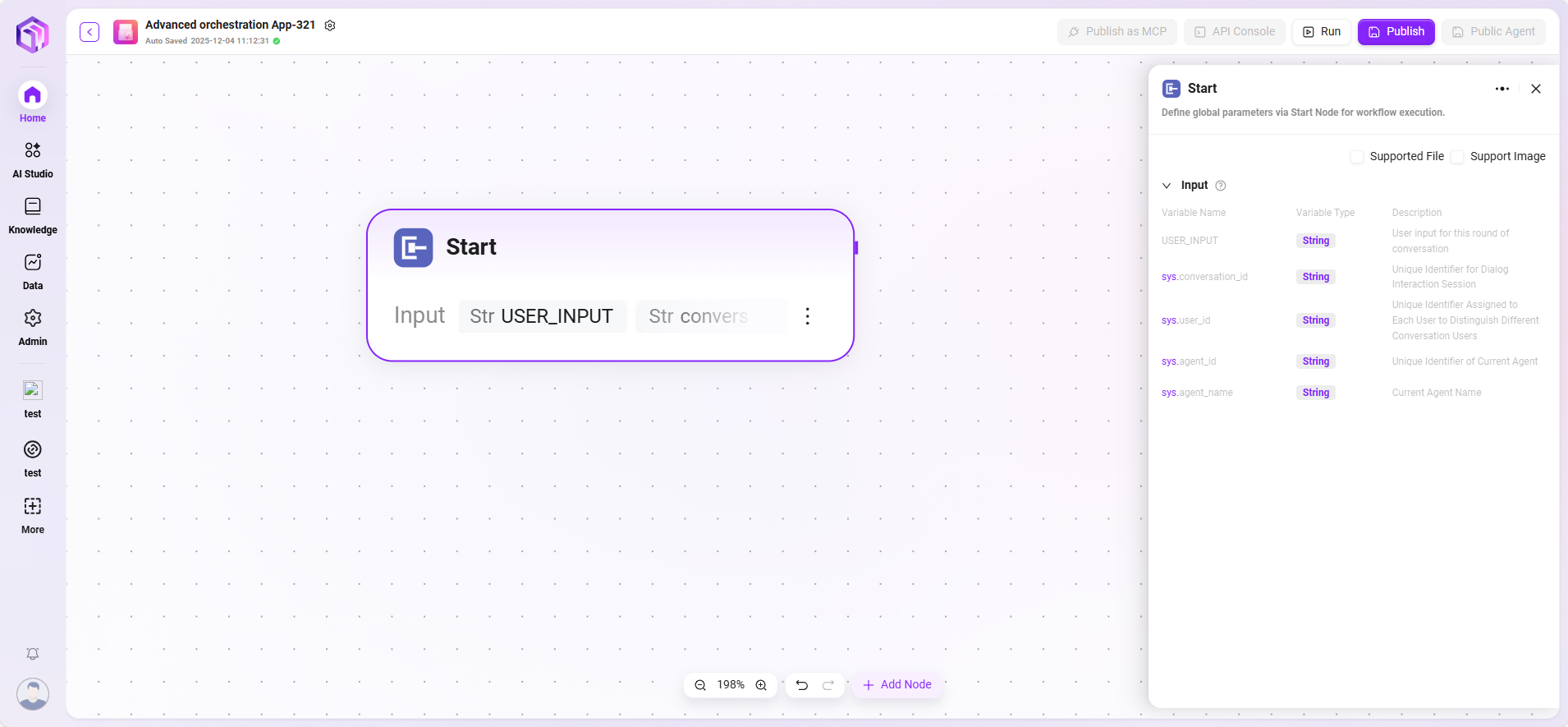
Start
The start node is the entry point of the workflow, used to set the information required to initiate the workflow.
- Function: Preset the basic information (input parameters) required to complete the task. When trigger conditions are met, the system automatically collects and passes these parameters to start the process.
- Processing Logic: By pass; passes input content directly to subsequent nodes.
- Output: All input content.
- Special Note (Application Mode): In this mode, the start node supports defining various complex input types, including file uploads (PDF, Excel, images, etc.) and structured data fields, providing a highly customized input interface for building professional applications.
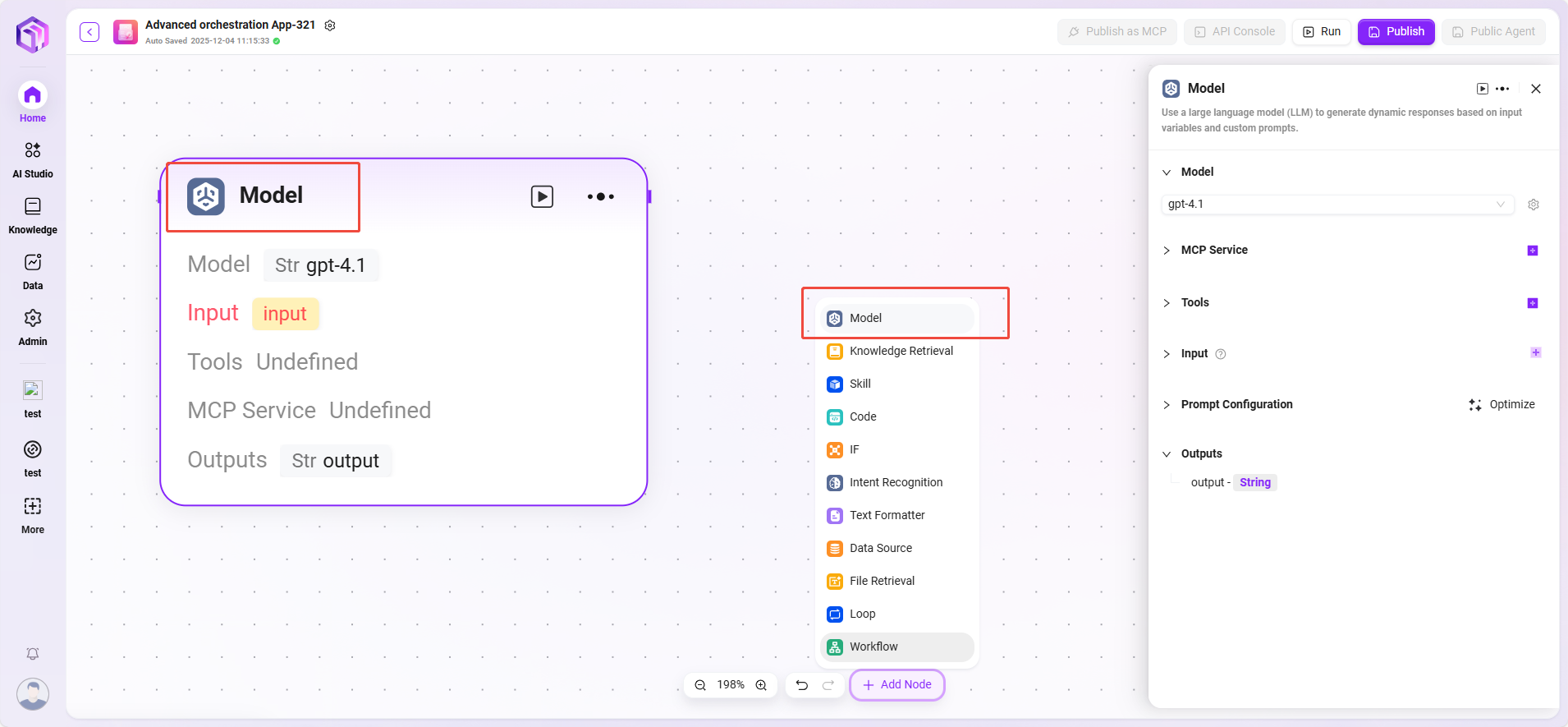
Model
Invoke large language models to generate responses using variables and prompts.
Input: Dropdown to select existing models, choose input variable names. Input Parameters: query (String, from upstream or user input). Configuration Parameters:
- One or more Tools
- Model
- GPT (GPT or other models)
- Temperature: Controls creativity; higher values yield more creative and random responses.
- Top P: Limits the range of words selected by "probability threshold," controlling response diversity.
- Max Reply Length: Limits the maximum number of characters the AI can reply with at one time.
- System Prompt: Hidden instructions for the AI to control overall style.
- User Prompt: Content or questions input by the user.
- History: Previous conversation rounds to maintain context understanding.
- Processing Logic: Inputs are processed by the large language model (LLM), which generates responses based on configuration.
- Output: Text content generated by the model.
💡 Tip: You must first connect to a preceding node to select variables from other nodes as input for the current node.
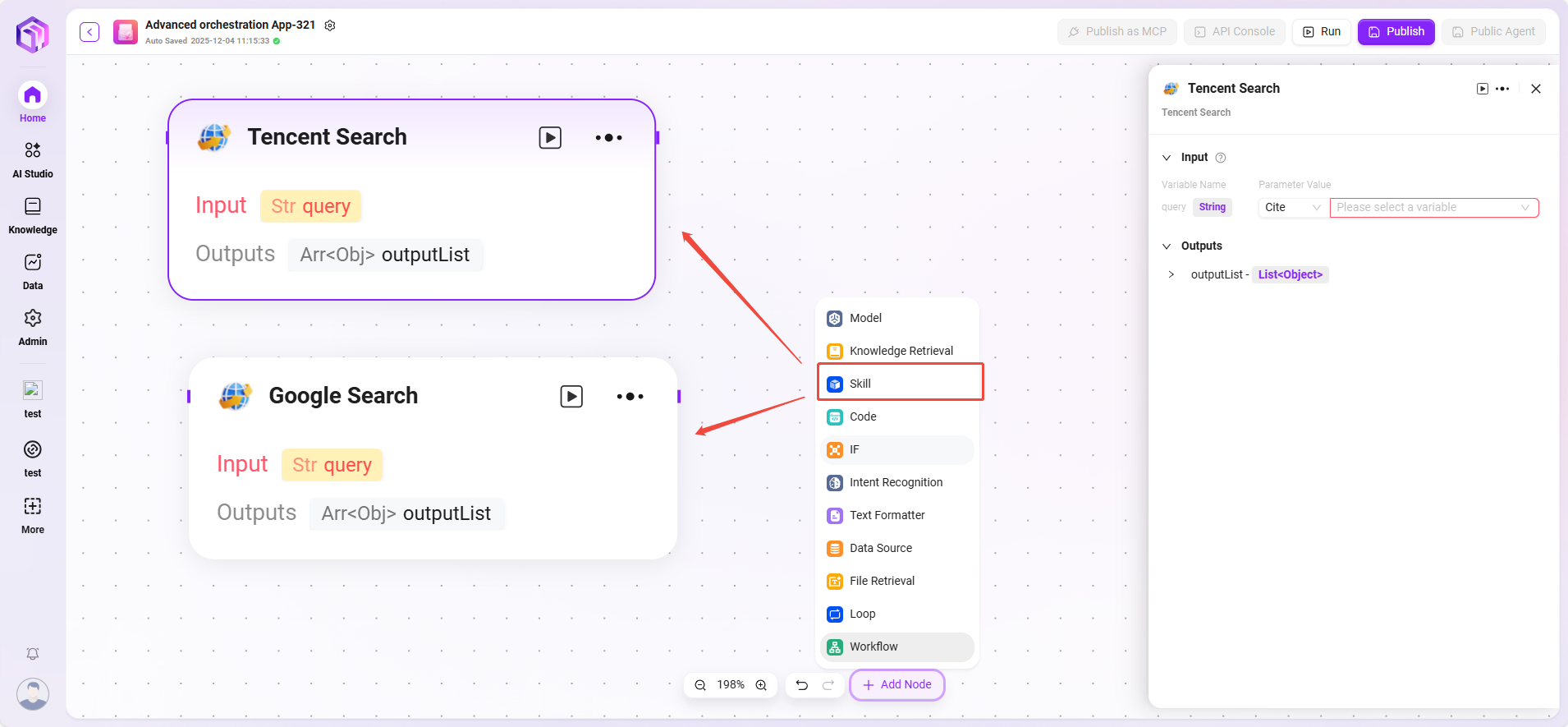
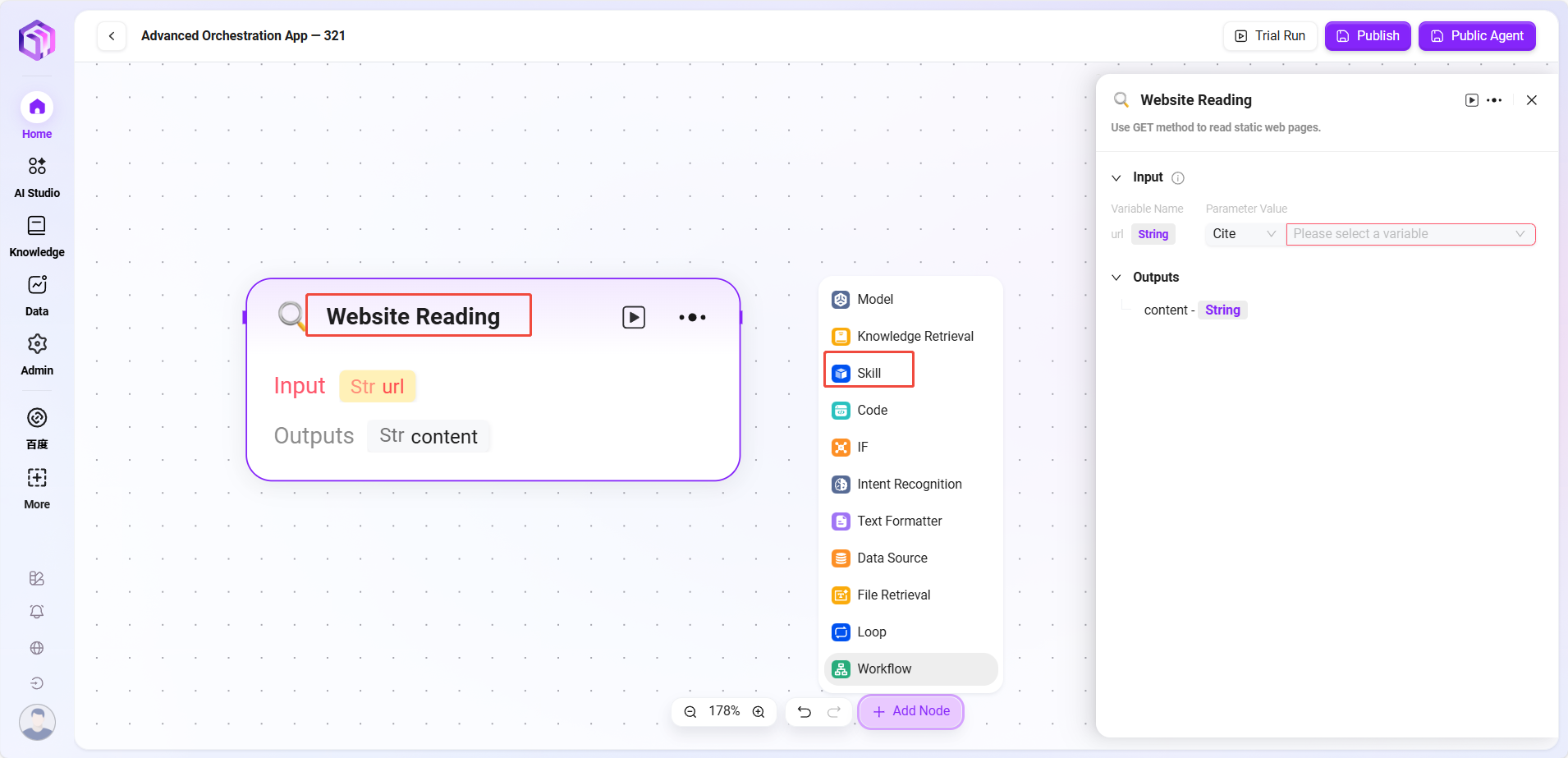
Skill (Examples)
- Website Reading: Can read static text on web pages (but cannot see dynamically loaded content).
- Text-to-Image Generation: Generates images based on descriptive text and returns the image URL.
- Tencent Search: Calls the search engine to return search results.
💡 Tip: In advanced orchestration mode, you can only add built-in skills; custom skills cannot be added.
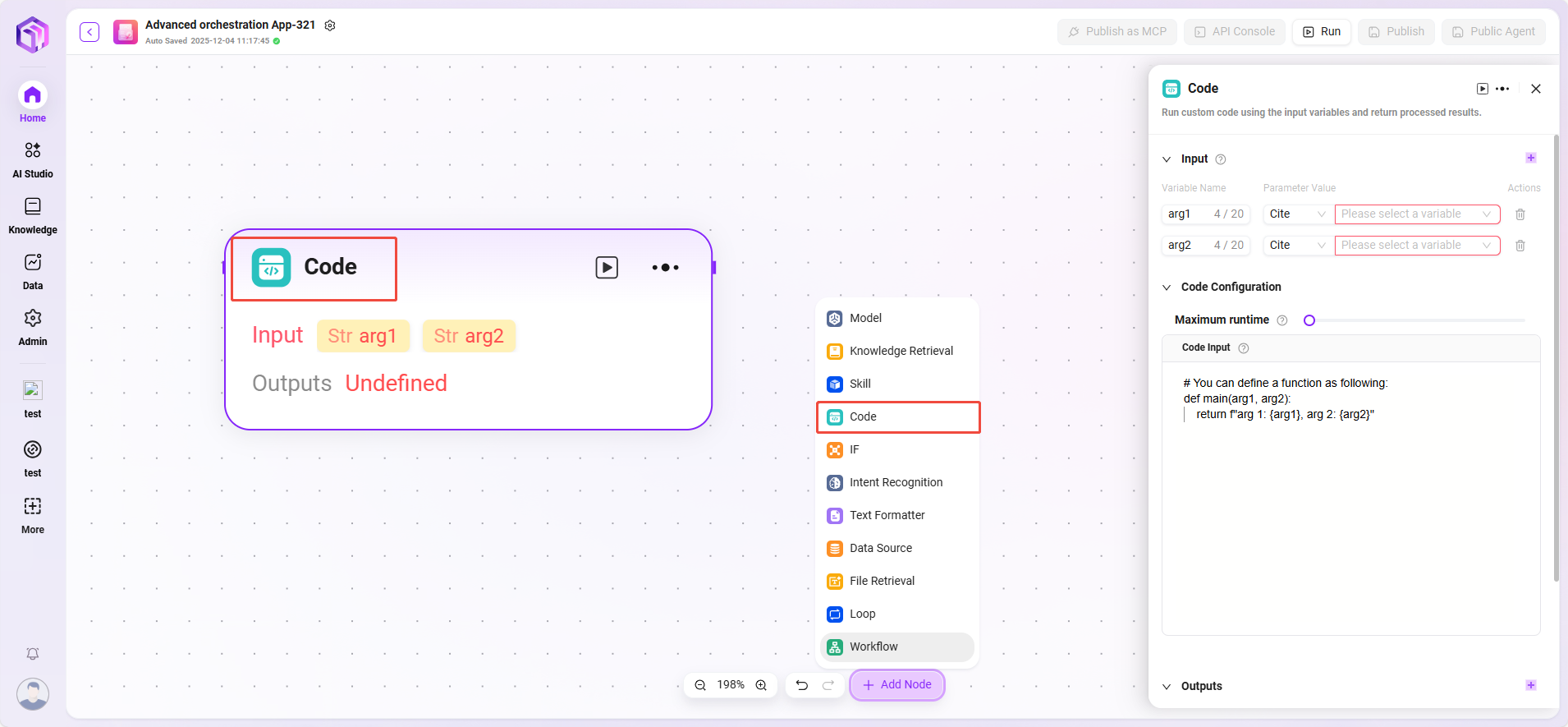
Code
Write code to process input variables and generate return values.
- Input: Receives externally passed variables, serving as the data entry point required for code execution and providing raw data for subsequent code processing.
- Input Parameters: query (string, code request from user or upstream).
- Configuration Parameters: Set parameters related to code execution.
- Maximum Runtime
- Code Input
- Processing Logic:
- Runs code in a secure sandbox environment (based on RestrictedPython or specified platform).
- Limits runtime and access permissions to avoid security risks.
- Output: After code processes the input data, the result is output as a specified variable, serving as the exit for code processing results.
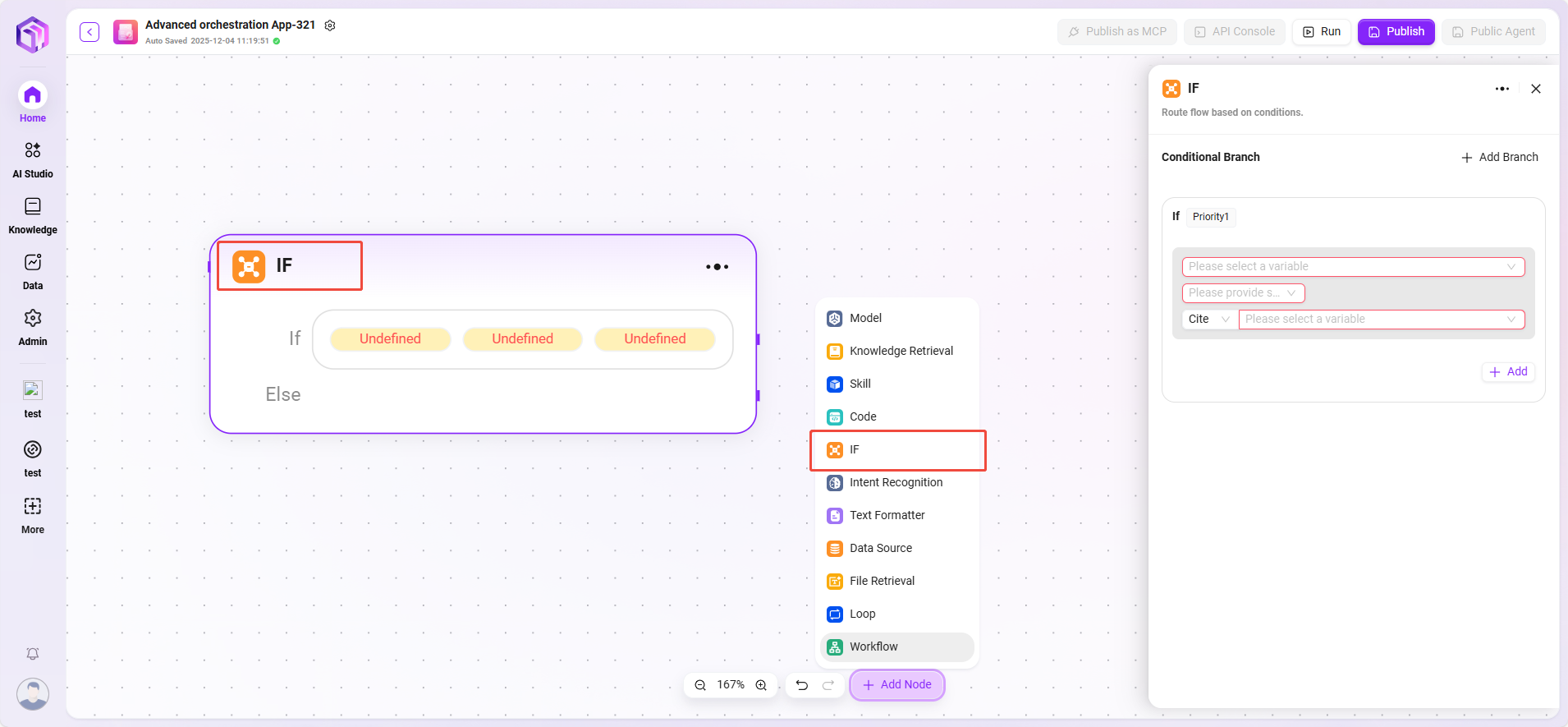
Selector
Acts as a conditional judgment in workflow orchestration. It connects multiple downstream branches and determines the execution path based on set conditions.
- Conditional Branches: Multiple conditions can be set, such as "if - priority 1." By configuring referenced variables, selecting conditions (e.g., equals, greater than, etc.), and comparison values, you can determine whether the condition is met. If so, the corresponding branch flow is executed.
- Processing Logic: Different paths are taken based on different conditions (if none are met, the Else path is taken).
- Output: No direct output; only determines the direction of the next node.
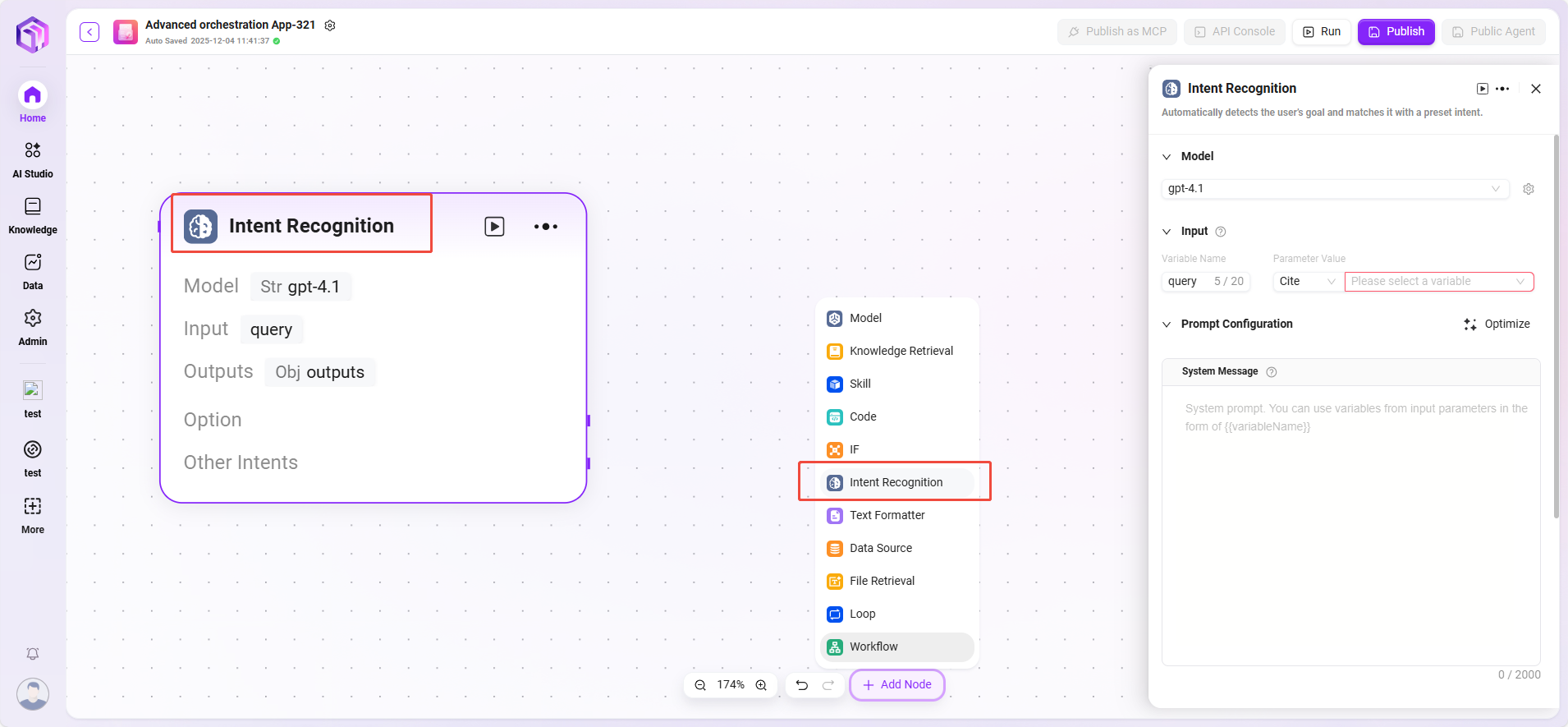
Intent Recognition
Intent recognition is a key step in natural language processing. This module analyzes user input to determine the true intent and matches it with preset options.
- Model: Select the model used for intent recognition; the model determines the capability and effectiveness of intent recognition.
- Intent Matching: User intent descriptions can be pre-entered as matching criteria, and other intents can be added. The system determines which preset intent the user input matches.
- Advanced Settings: System prompt content can be set, and input variables can be referenced to optimize prompt effectiveness; the number of historical memories can also be set, allowing the model to refer to past conversation information to improve recognition accuracy.
- Processing Logic: Determines the user's true intent and classifies the input into the corresponding category.
Knowledge Base Retrieval
- Input: By defining variable names and setting parameter values, provides keywords and other raw data for knowledge base retrieval.
- Processing Logic: Retrieves the knowledge base based on input and parameters, returning fragments or FAQs.
- Knowledge Base: Select a specific knowledge base as the retrieval scope; the system will search for matching information within this range.
- Max Recall Quantity: Set the maximum number of matching results to return from the knowledge base to avoid excessive data.
- Output: Outputs the matching information retrieved from the knowledge base as specified variables for use in subsequent flows.
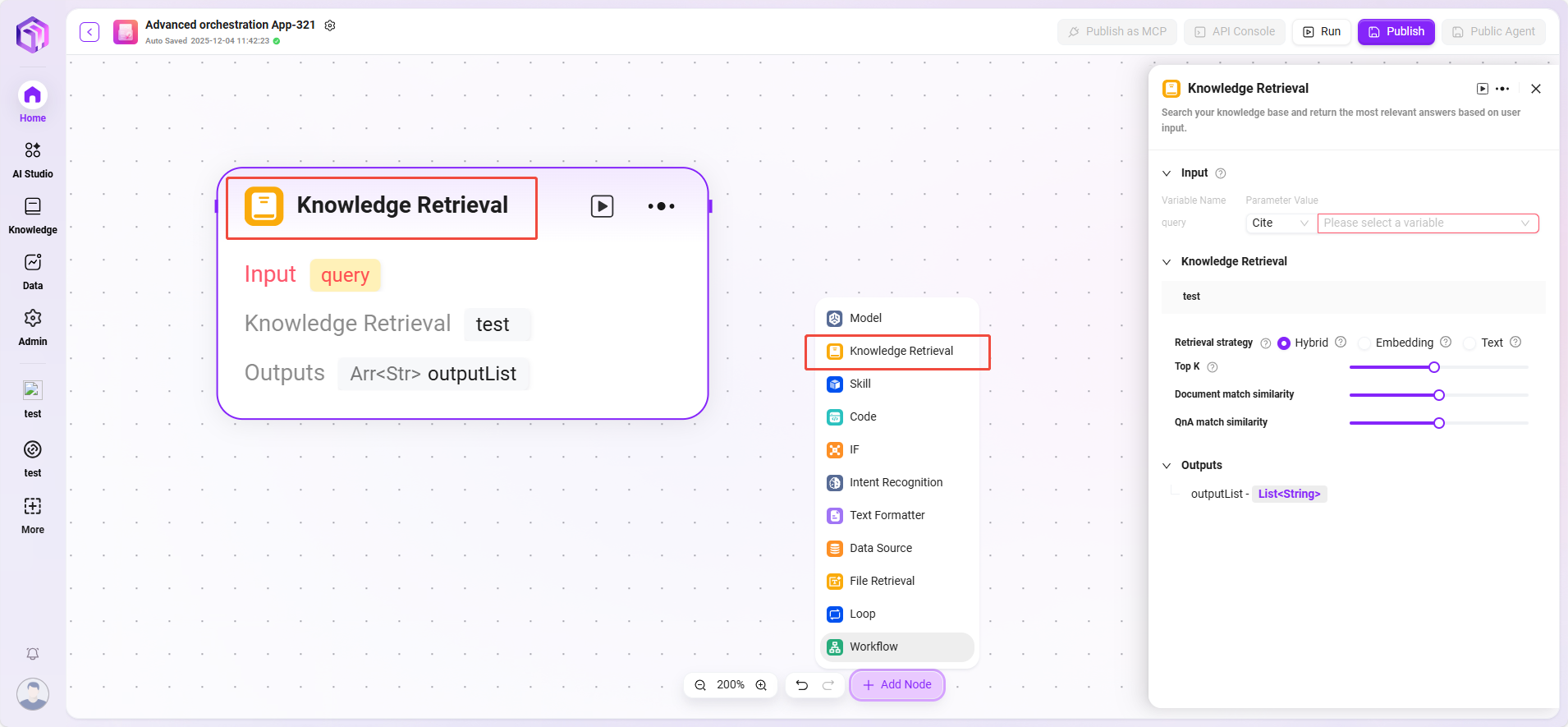
Text Formatter
Mainly used to process the format of string-type variables.
- Input: Variable names can be defined, and parameter values can be obtained by reference, providing raw string data for subsequent text processing.
- Processing Logic: Simple processing of text.
- String concatenation
- String splitting
- String Concatenation: Provides a text editing area; input variables can be referenced by variable name as needed to concatenate multiple strings and perform other formatting operations.
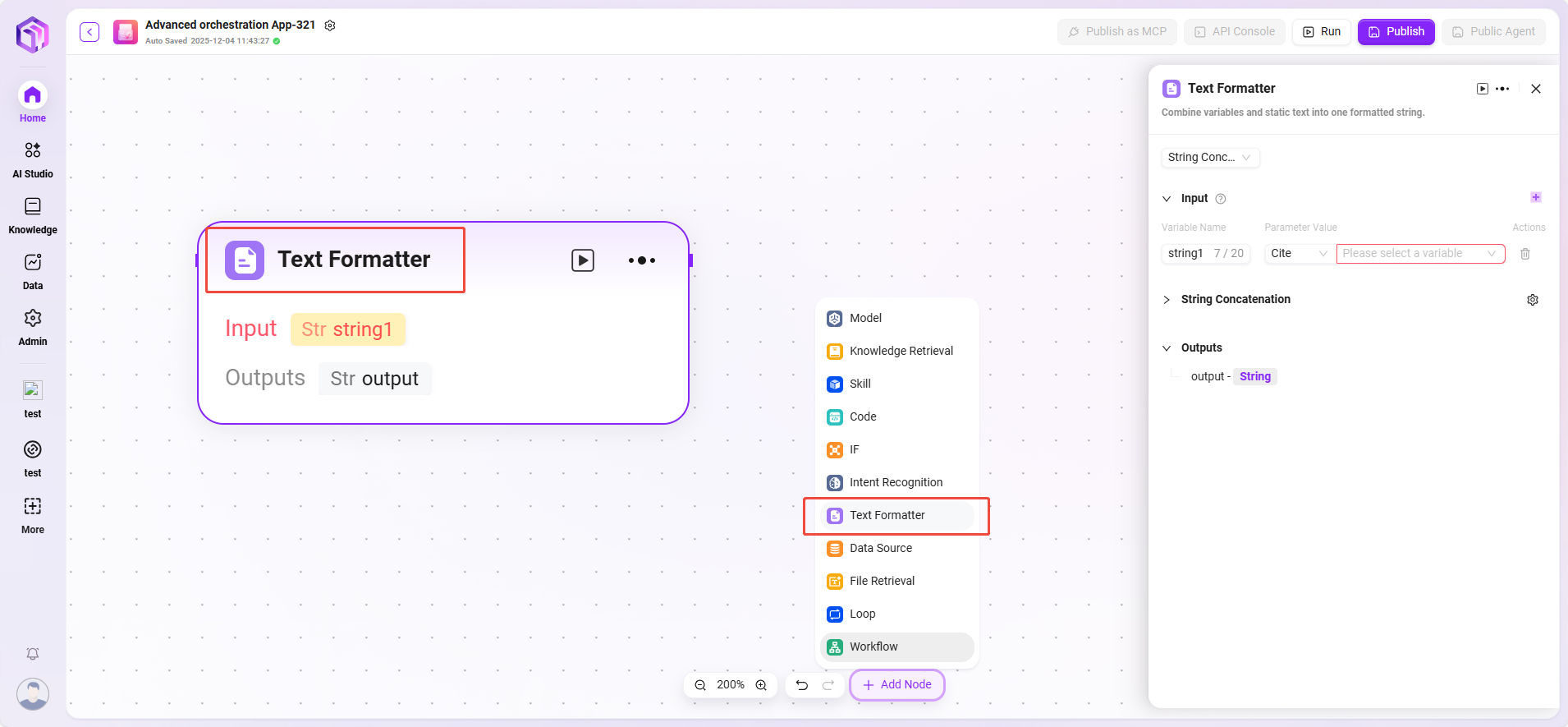
File Retrieval
File retrieval is a functional module for searching and processing file content.
- Input: By defining variable names and referencing parameter values, provides keywords and other input information for file content search.
- File: Files to be processed can be added to this node to determine the scope of retrieval.
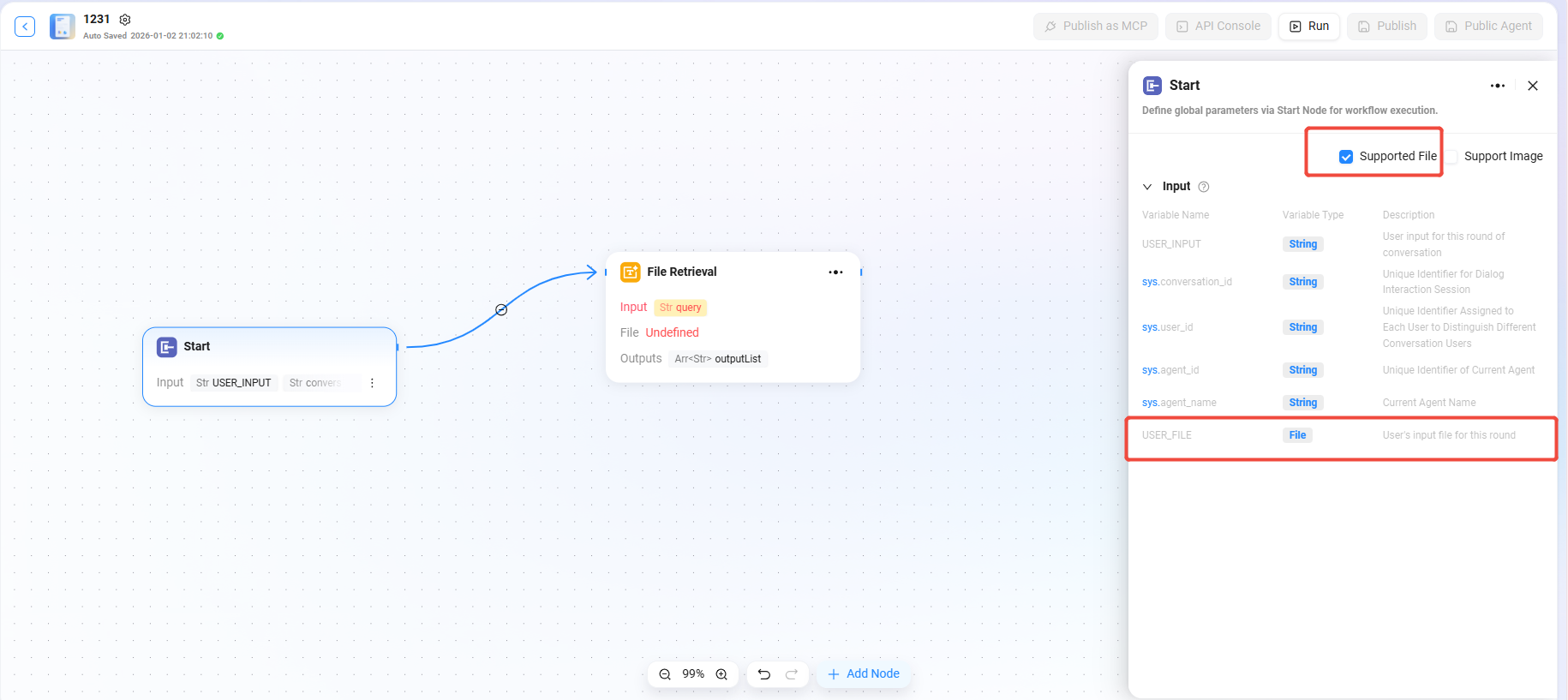
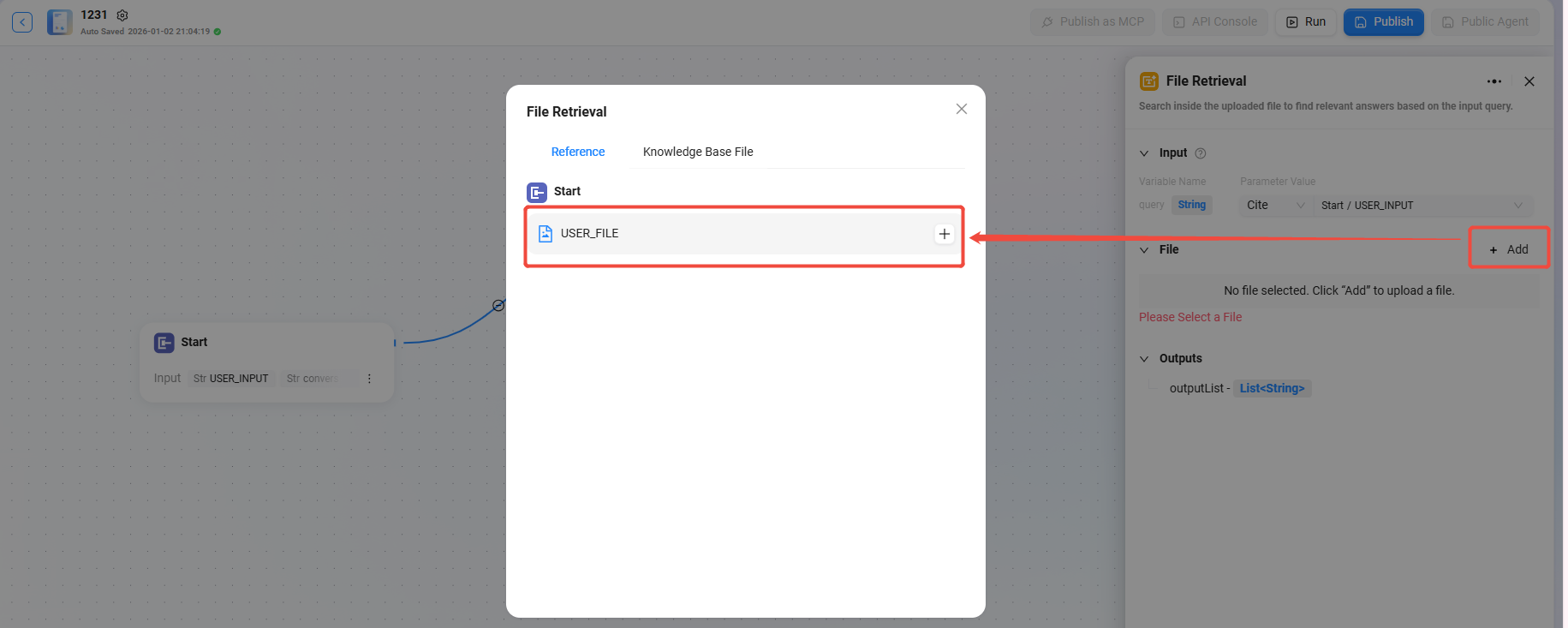
Configuration File Retrieval
- First, you need to check “Support Files” in the “Start” node
- After checking it, a variable named “USER_FILE” will appear in the Start node, which represents the file provided by the user in the current turn
- Then, connect the “Start” node to the “File Retrieval” node
- After the connection, the File Retrieval node can add “USER_FILE” as the file to be retrieved
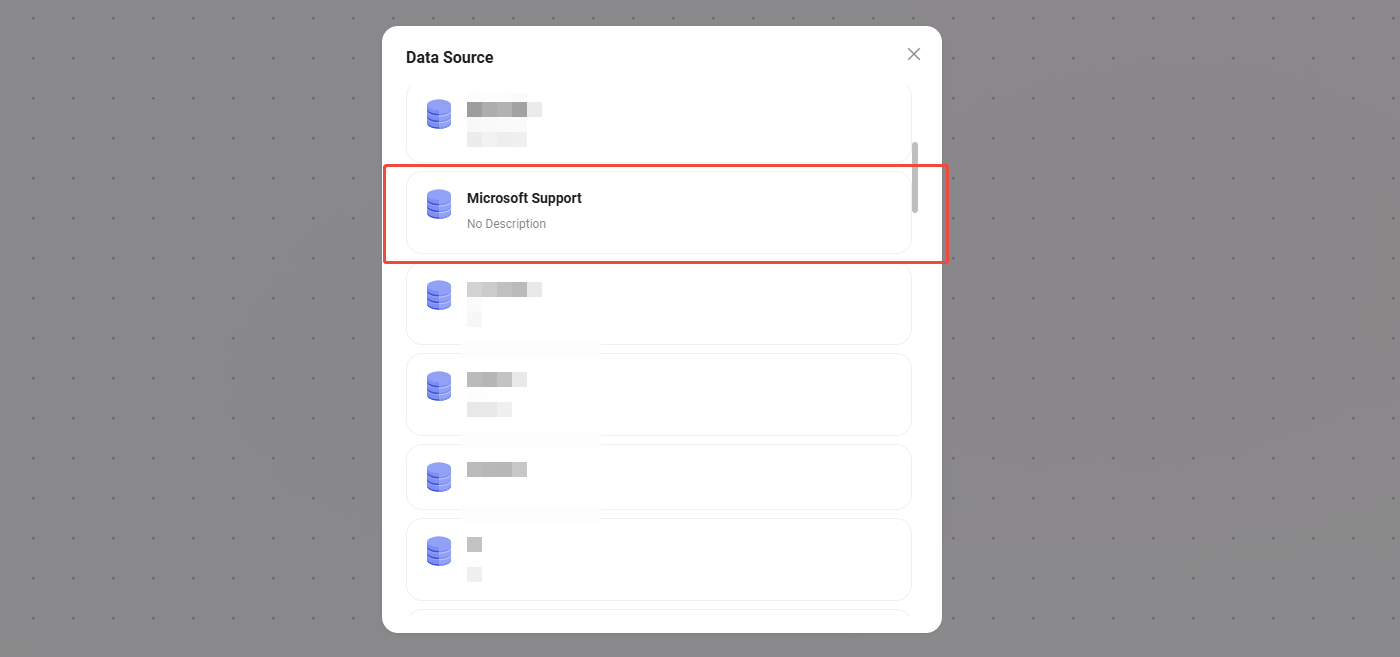
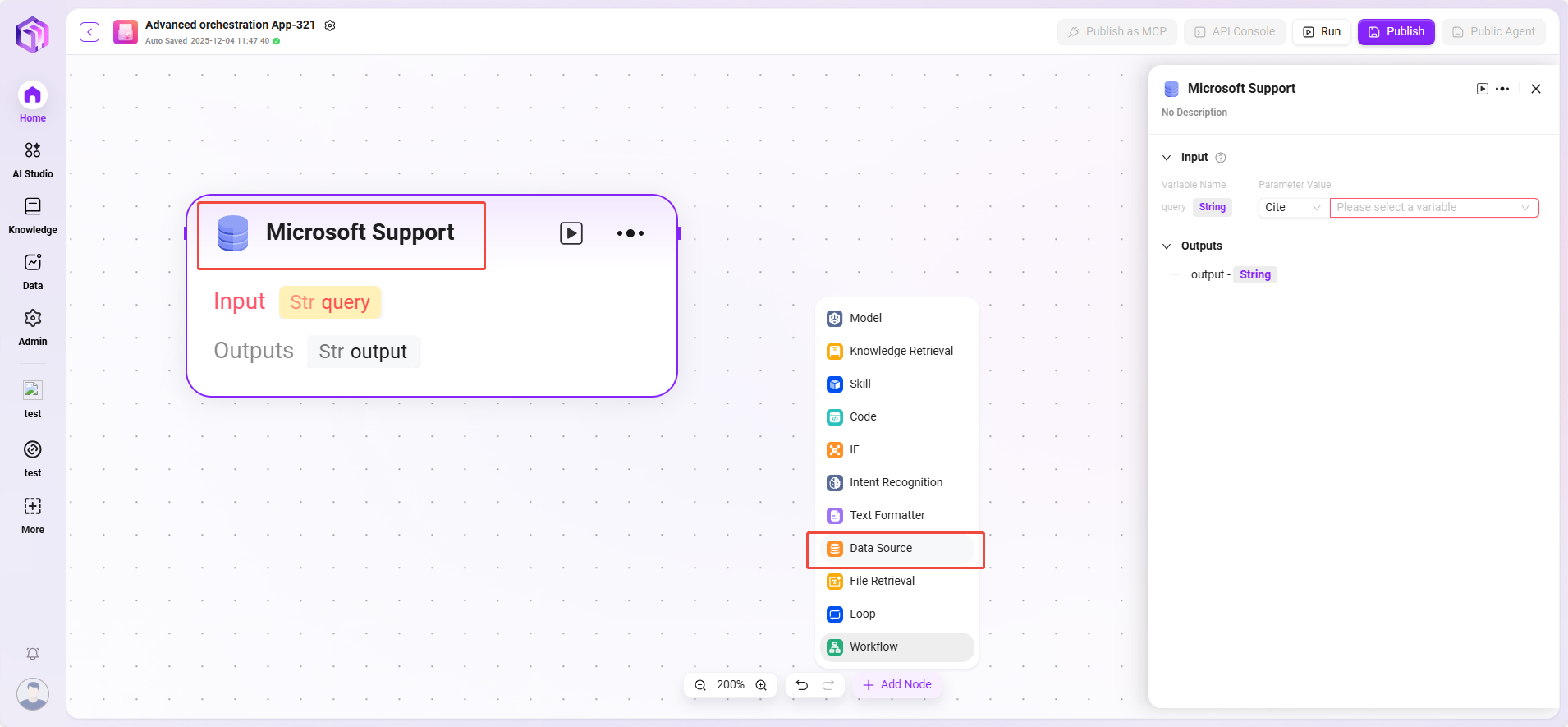
Data Source
- Data Source: Select the data source to connect.
- Processing Logic: Converts natural language into SQL to query the database and return results.
- Output: Outputs data from the data source to the next node.
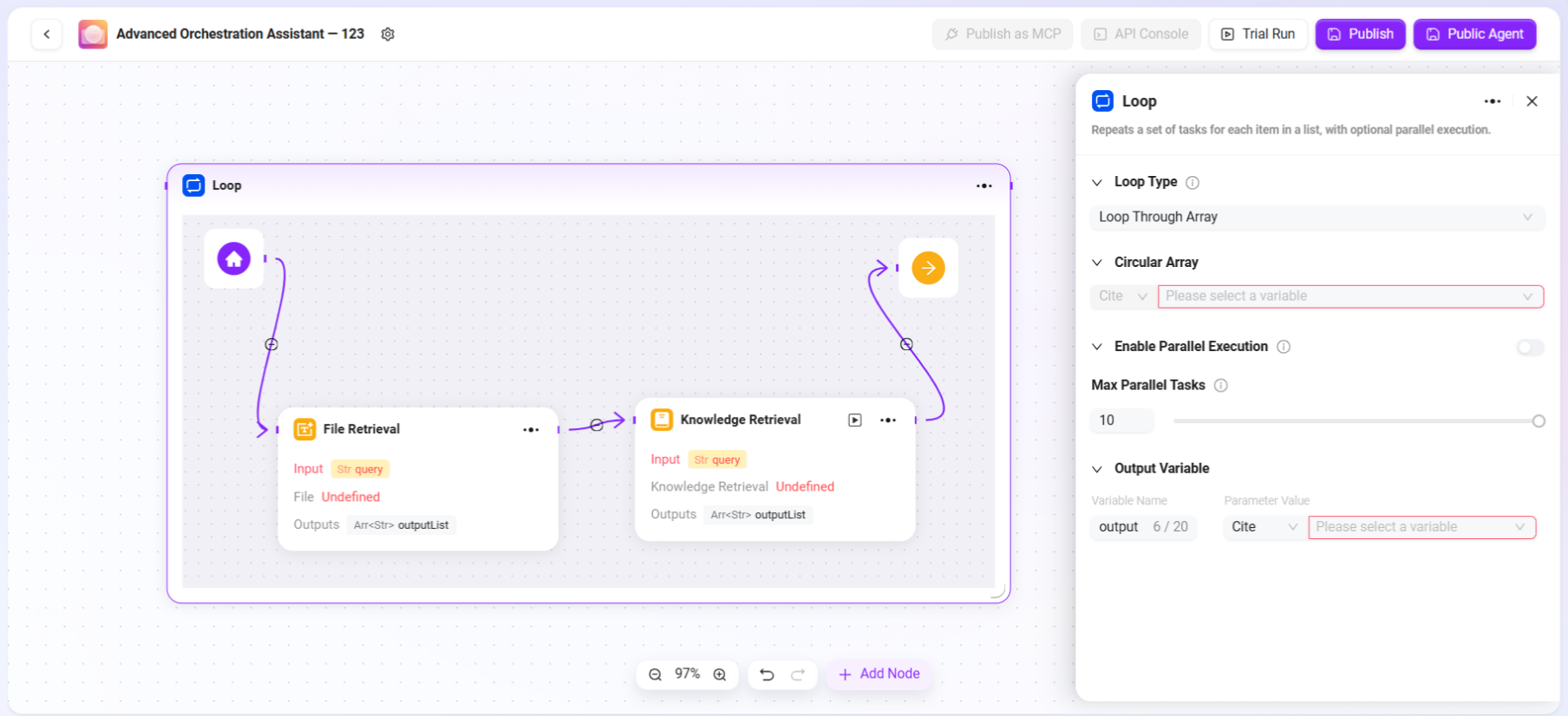
Loop
Used to repeatedly execute a set of tasks according to a specified number of times or data set. By configuring different loop modes, batch processing or repeated operations can be flexibly implemented.
- Loop Type: Supports two modes
- Array Loop: Executes tasks sequentially for each element in the input array.
- Numeric Loop: Executes tasks repeatedly according to the set number of times.
- Loop Value/Array:
- When "Numeric Loop" is selected, a specific number must be entered, e.g., 2, meaning the task will be executed 2 times.
- When "Array Loop" is selected, an array variable must be provided; the system will extract each element from the array as input to execute the task.
- Parallel Execution: Optional feature. If enabled, the system will process multiple loop tasks simultaneously to improve efficiency. Users can set the maximum parallelism to control resource usage.
Workflow Example
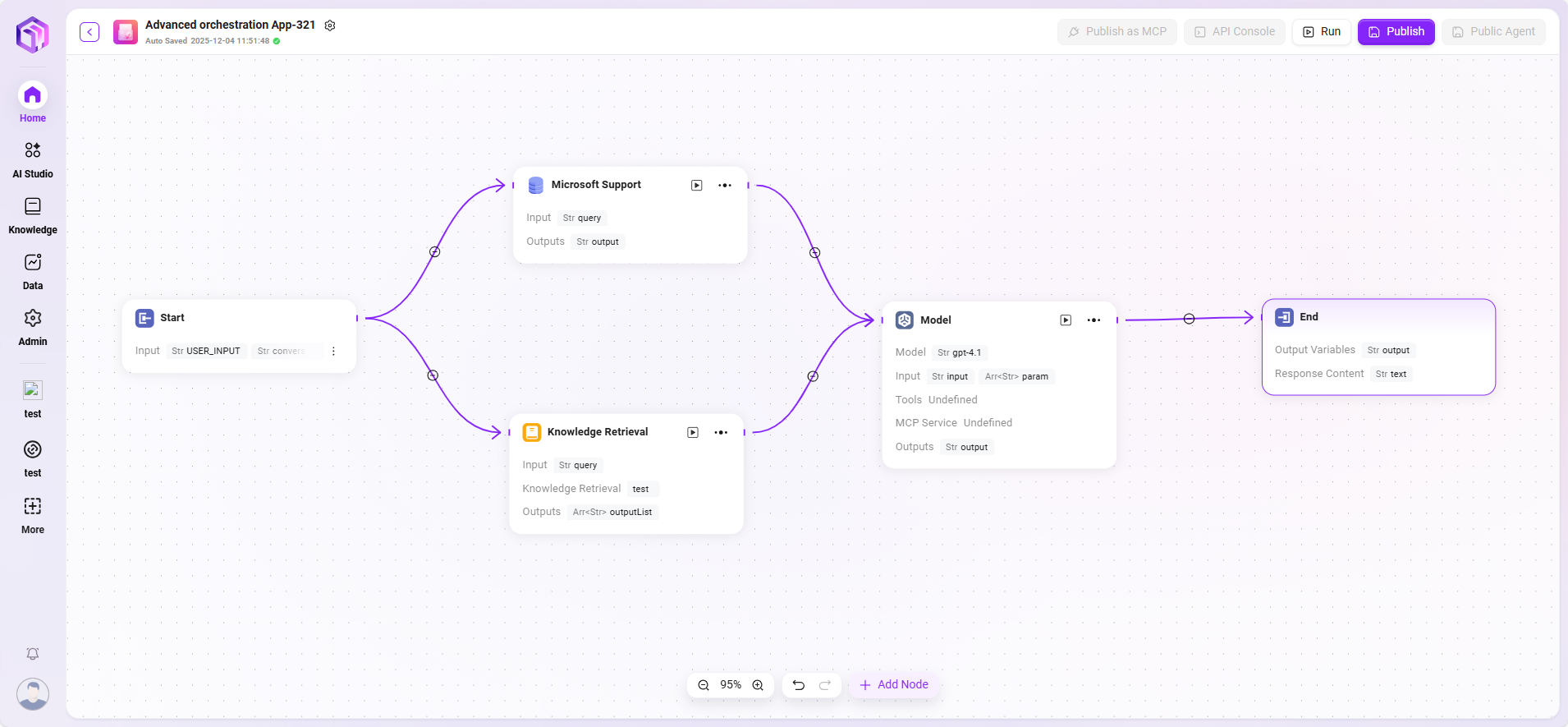
In this scenario, the workflow feature is used to build a complete "Microsoft Support Ticket Issue Analytics" process. The specific workflow is as follows:
- Start Node
The starting point of the process, included by default. - Data Source Node
Used to connect the raw data required for ticket analysis. - Knowledge Base Node
Connects knowledge documents containing analytical reference materials, serving as the theoretical support for AI analysis. - Model Node
Based on the AI model, combines data source and knowledge base content for comprehensive analysis, generating ticket issue analysis results. - End Node
The endpoint of the process, outputs the analysis results from the model node. This node is included by default.
The data source node and knowledge base node are configured in parallel, while the model node aggregates and processes information from both, ensuring the output results have both data support and theoretical backing.
Final result:
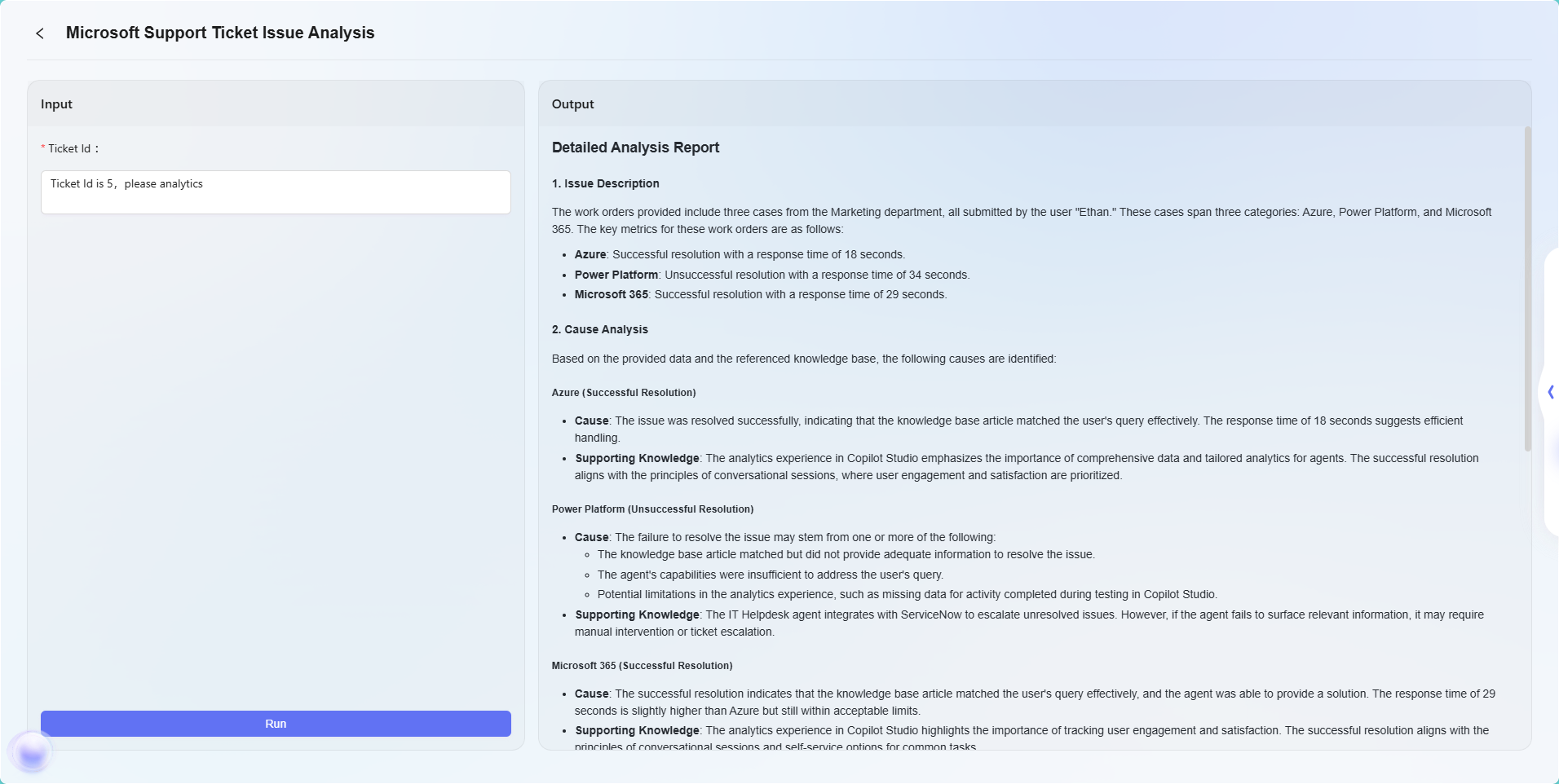
Note: This example is only a basic demonstration of the workflow feature. Workflow orchestration is highly flexible and extensible. By combining various nodes, extremely complex business logic and automated processes can be implemented, adapting to a wide range of business scenario requirements.