Workflow Creation Agent
Workflow Creation - Advanced Agent
- Select "Advanced Agent" (The creation steps are the same as creating a regular agent)
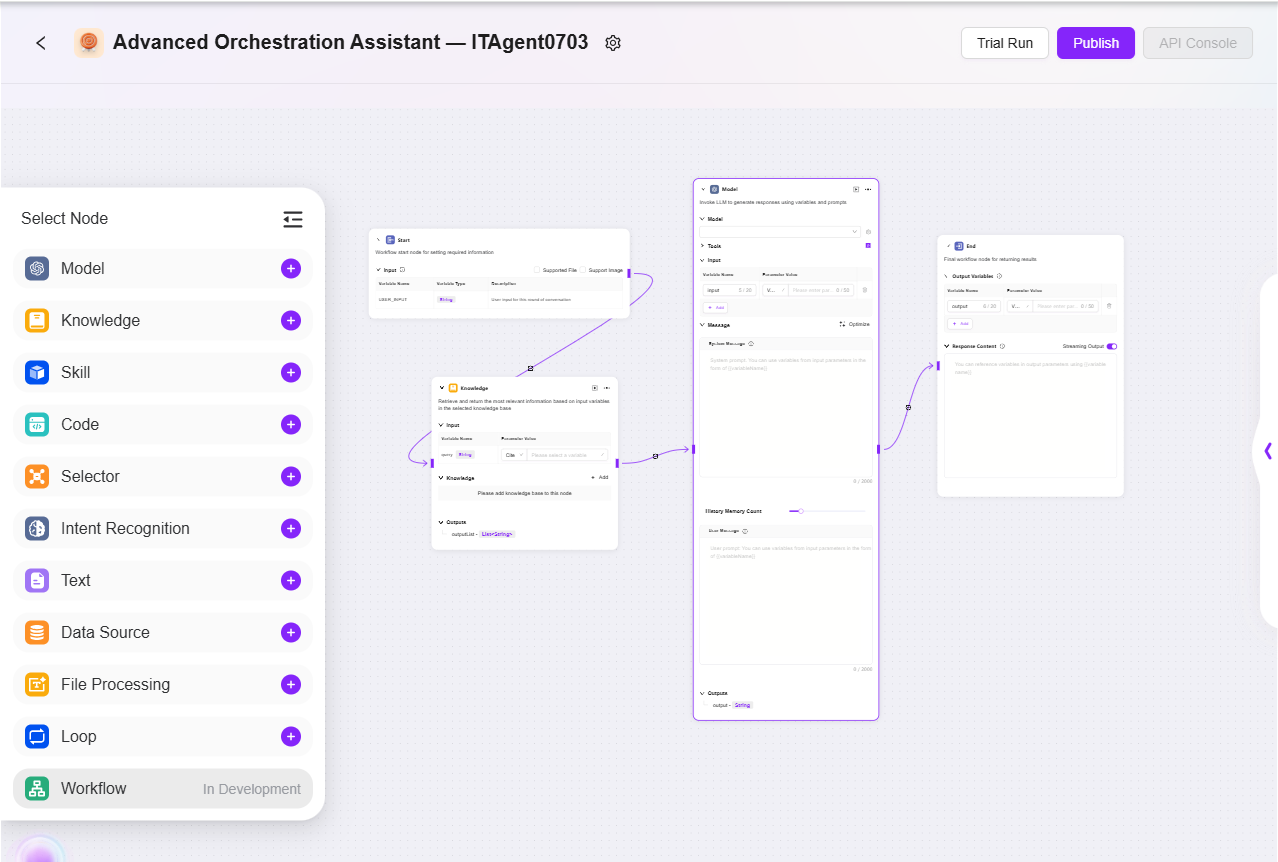
- Configure the workflow according to actual business needs:
- Start, End: Built-in input/output modules, allowing customization of input/output parameters and fields
- Model: Select the model to use in this module, input variables obtained from other modules, edit prompts and output messages, and save them as variables
- Skill: Select one skill to perform input/output actions through that skill
- Data Source: Select a data source to add variable content that can be referenced
- Code: Based on the output variables from other modules, customize and create code functions
- Knowledge: In the selected knowledge base, recall the most relevant information based on input variables and return it
- Selector: Connect multiple downstream branches; if the set condition is met, only the corresponding branch will run. If none are met, only the "otherwise" branch will run
- Intent Recognition: Used for recognizing user input intent and matching it with preset intent options
- Text: Used for formatting multiple character-type variables
- Detailed Node Introduction
-
Start
-
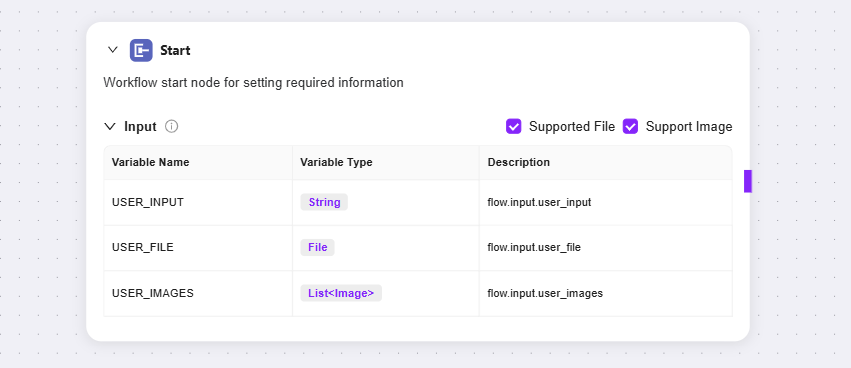
Start Node: The starting node of the workflow, used to set the information required to initiate the workflow
-
Input: Simply put, it tells the LLM in advance what basic information (input parameters) is needed to complete a task. When used, the LLM will remember these information requirements. Once it detects the opportunity to start the task in the conversation, it will automatically call these preset parameters, place them in the corresponding positions, and thus start the entire process.
-
-
Model
-
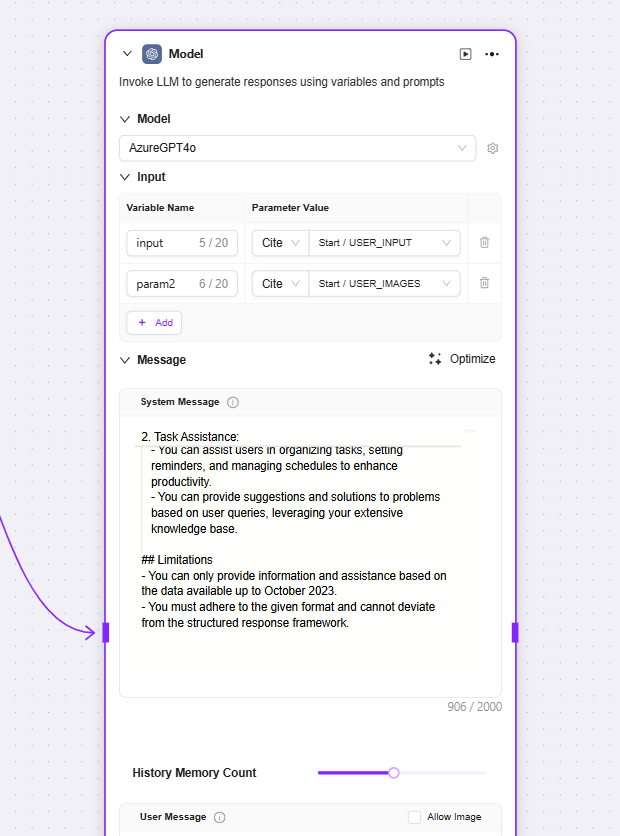
Model: Calls a large language model to generate replies using variables and prompts
-
Input: Dropdown to select an existing model and choose input variable names
-
Message: Provides high-level guidance for the conversation
-
User Message: Provides instructions, queries, or any text-based input to the model
-
💡 Tip: You need to connect to a previous node first to select variables from other nodes as input variables for the current node
-
Skill
-
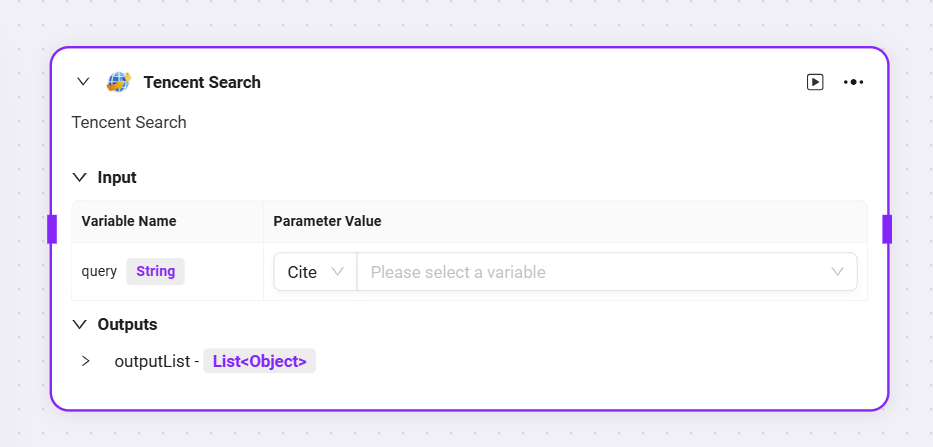
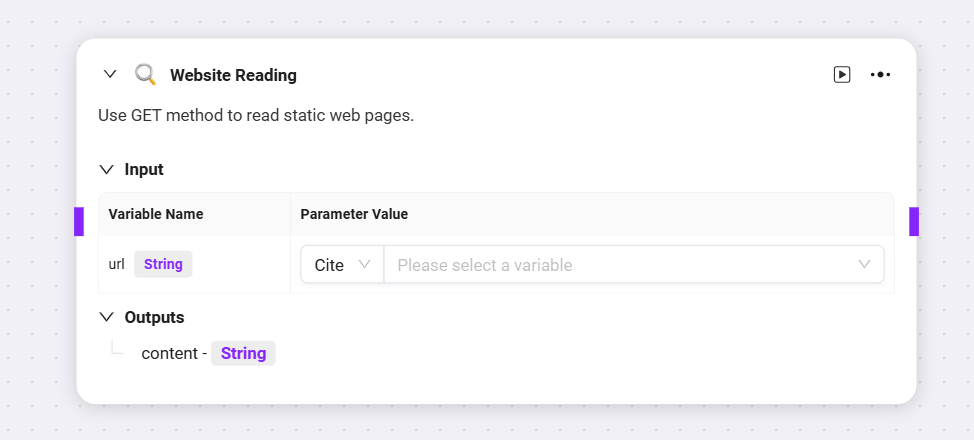
Currently, three default skills can be added to advanced orchestration: Web Search, Text-to-Image, Webpage Reading
-
You can input the variable from the previous node as the query or URL for each, and obtain the corresponding output variable
-
-
Code
-
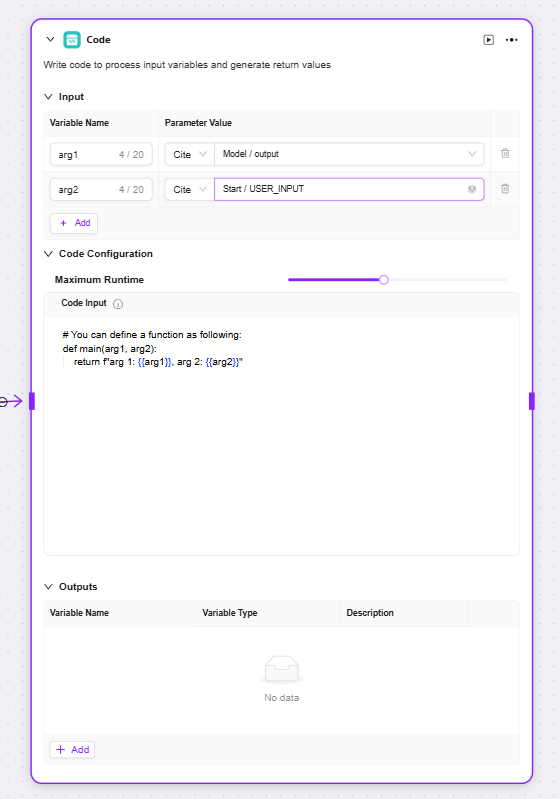
Code: Write code to process input variables and generate return values
-
Input: Used to receive externally passed-in variables, serving as the data entry required for code execution and providing raw data for subsequent code processing
-
Code Configuration: Set parameters related to code execution (such as maximum runtime), and provide a code editing area to write logic for processing input variables
-
Outputs: After the code processes the input data, the result is output as a specified variable, serving as the exit for the code processing result
-
-
Selector
-
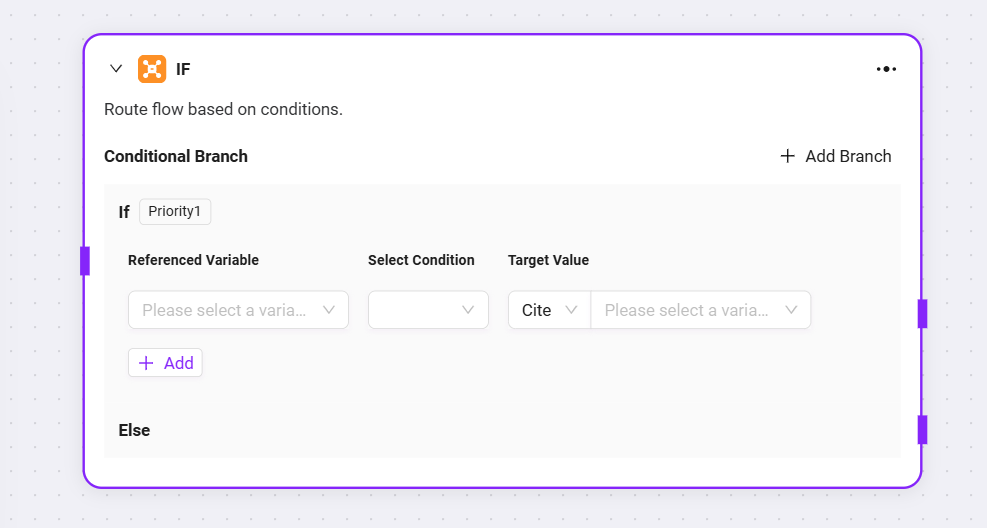
Selector: Acts as a conditional judgment in workflow orchestration. It connects multiple downstream branches and determines the execution path based on set conditions
-
Conditional Branch: Multiple conditions can be set, such as "if - priority 1". By configuring referenced variables, selecting conditions (such as equals, greater than, etc.), and comparison values, you can determine whether the condition is met. If so, the corresponding branch process will run.
-
-
Knowledge Base
-
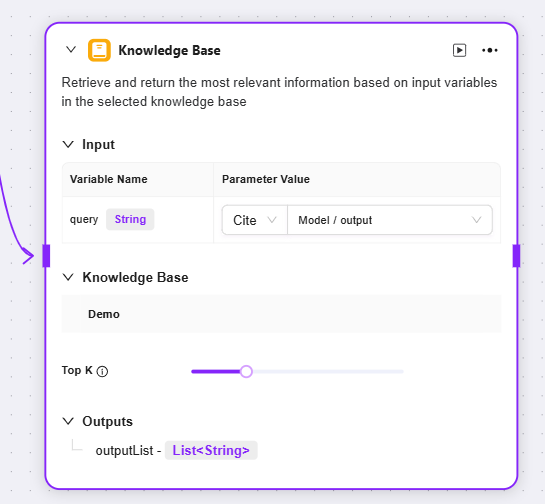
Input: By defining variable names and setting parameter values, provide original data such as search keywords for knowledge base retrieval
-
Knowledge Base: Select a specific knowledge base as the search scope; the system will search for matching information within this range
-
Maximum Recall Quantity: Set the maximum number of matching results returned from the knowledge base to avoid returning too much data
-
Outputs: Output the matching information retrieved from the knowledge base as a specified variable for use in subsequent processes
-
-
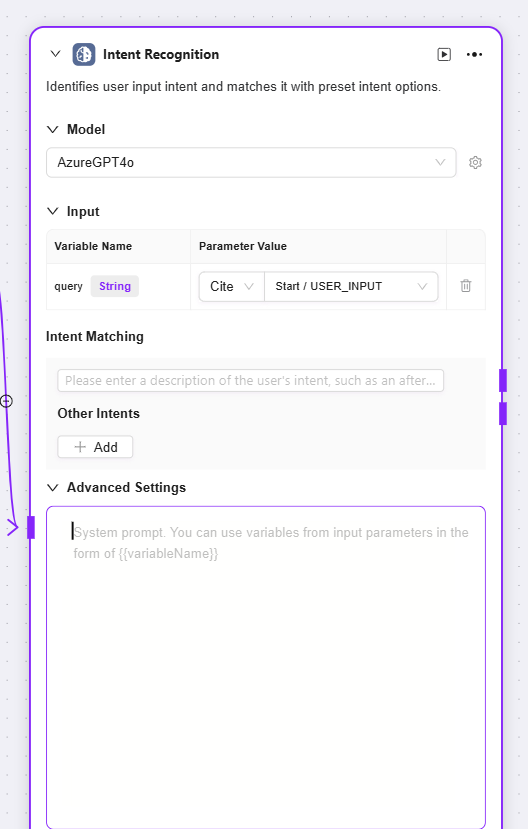
Intent Recognition
-
Intent Recognition: A key step in natural language processing, this module analyzes user input to determine their true intent and matches it with preset options
-
Model: Select the model used for intent recognition, which determines the capability and effectiveness of intent recognition
-
Intent Matching: You can pre-enter user intent descriptions as matching criteria, and also add other intents. The system will determine which preset intent the user input matches
-
Advanced Settings: Allows you to set system prompt content, reference input variables to optimize prompt effects, and set the number of historical memory entries so the model can refer to past conversation information to improve recognition accuracy
-
-
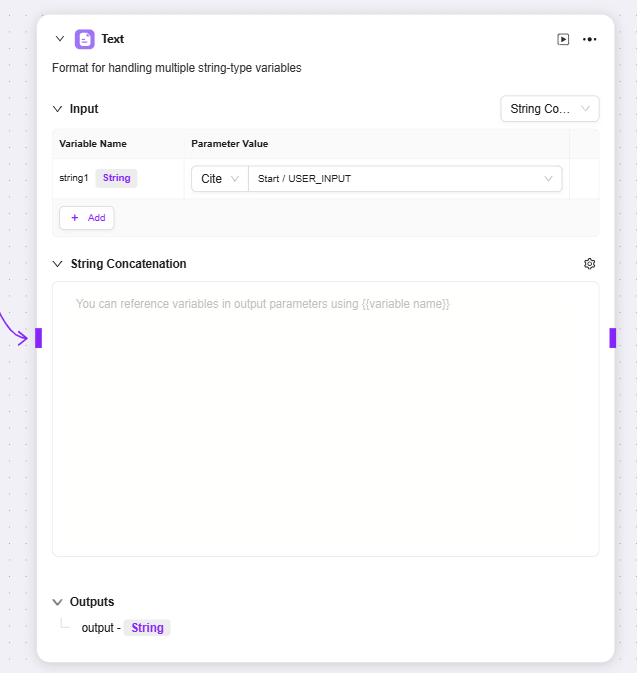
Text
-
Text: Mainly used for formatting string-type variables
-
Input: You can define variable names and obtain parameter values by reference, providing original string data for subsequent text processing
-
String Concatenation: Provides a text editing area where you can reference input variables by variable name as needed to concatenate multiple strings or perform other formatting
-
-
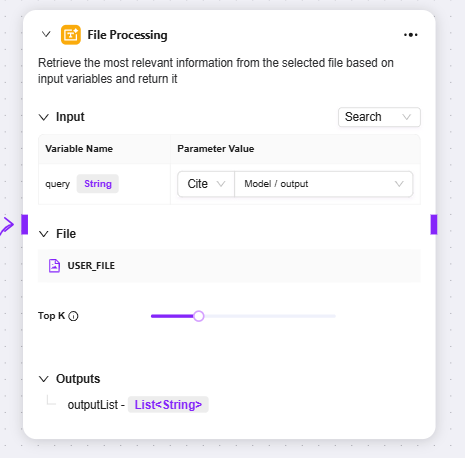
File Processing
-
File Processing: A functional module for searching and other operations on file content
-
Input: By defining variable names and referencing parameter values, provide input information such as search keywords as the basis for file content search
-
File: You can add files to be processed to this node to determine the file search scope
-
-
Data Source
-
Data Source: Select the data source to connect
-
Outputs: Output the data from the data source to the next node.
-
Workflow Example
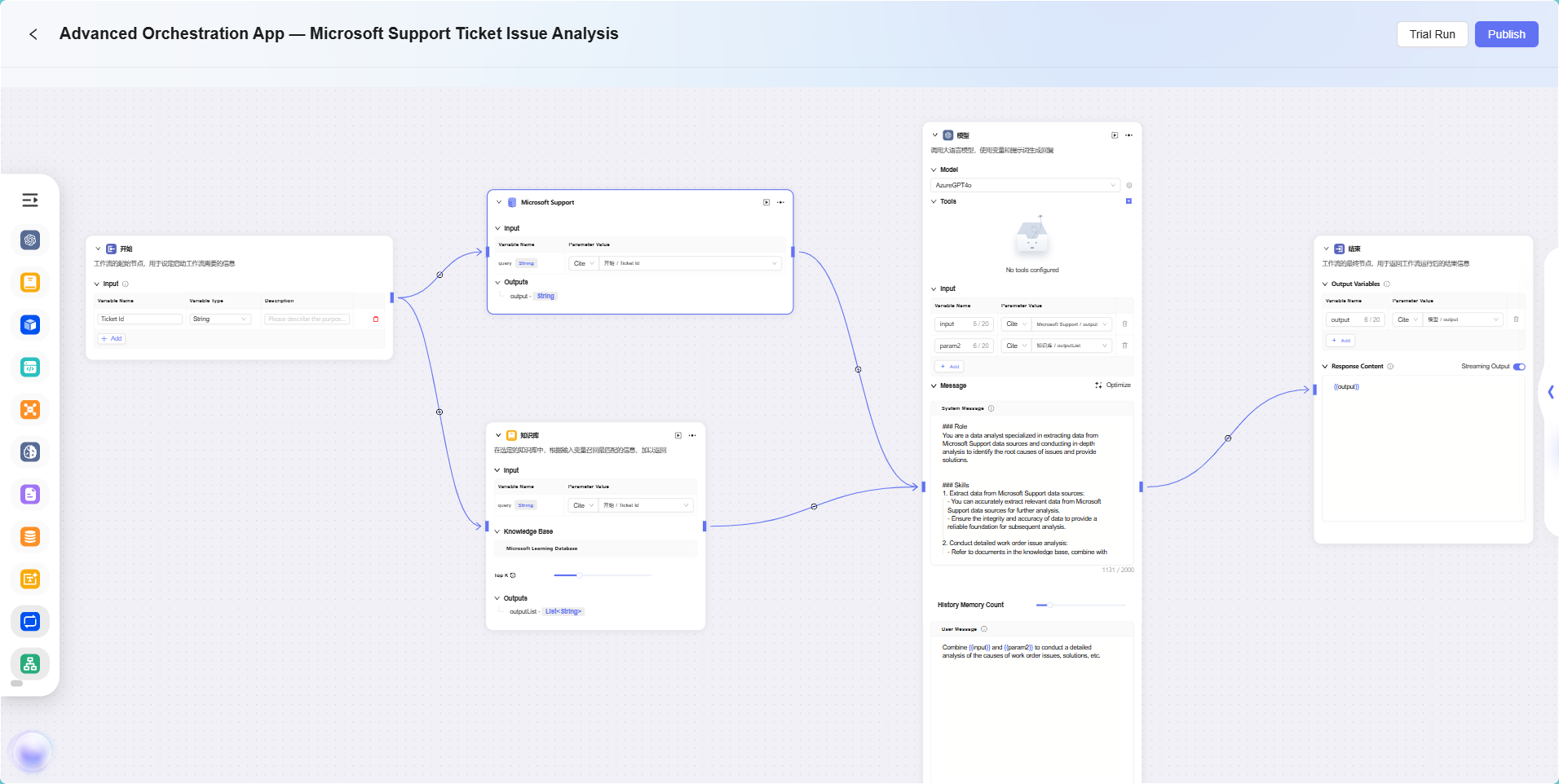
In this scenario, the workflow feature is used to build a complete "Microsoft Support Ticket Issue Analytics" process. The specific workflow is as follows:
-
Start Node
The starting point of the process, included by default in the system. -
Data Source Node
Used to access the raw data required for ticket analysis. -
Knowledge Base Node
Connects to knowledge documents containing reference materials for analysis, serving as the theoretical support for AI analysis. -
Model Node
Based on the AI model, combines data source and knowledge base content for comprehensive analysis and generates ticket issue analysis results. -
End Node
The endpoint of the process, outputs the analysis results from the model node. This node is included by default in the system.
The data source node and knowledge base node are configured in parallel, while the model node aggregates and processes information from both to ensure that the output results have both data support and theoretical backing.
The final effect is as follows:
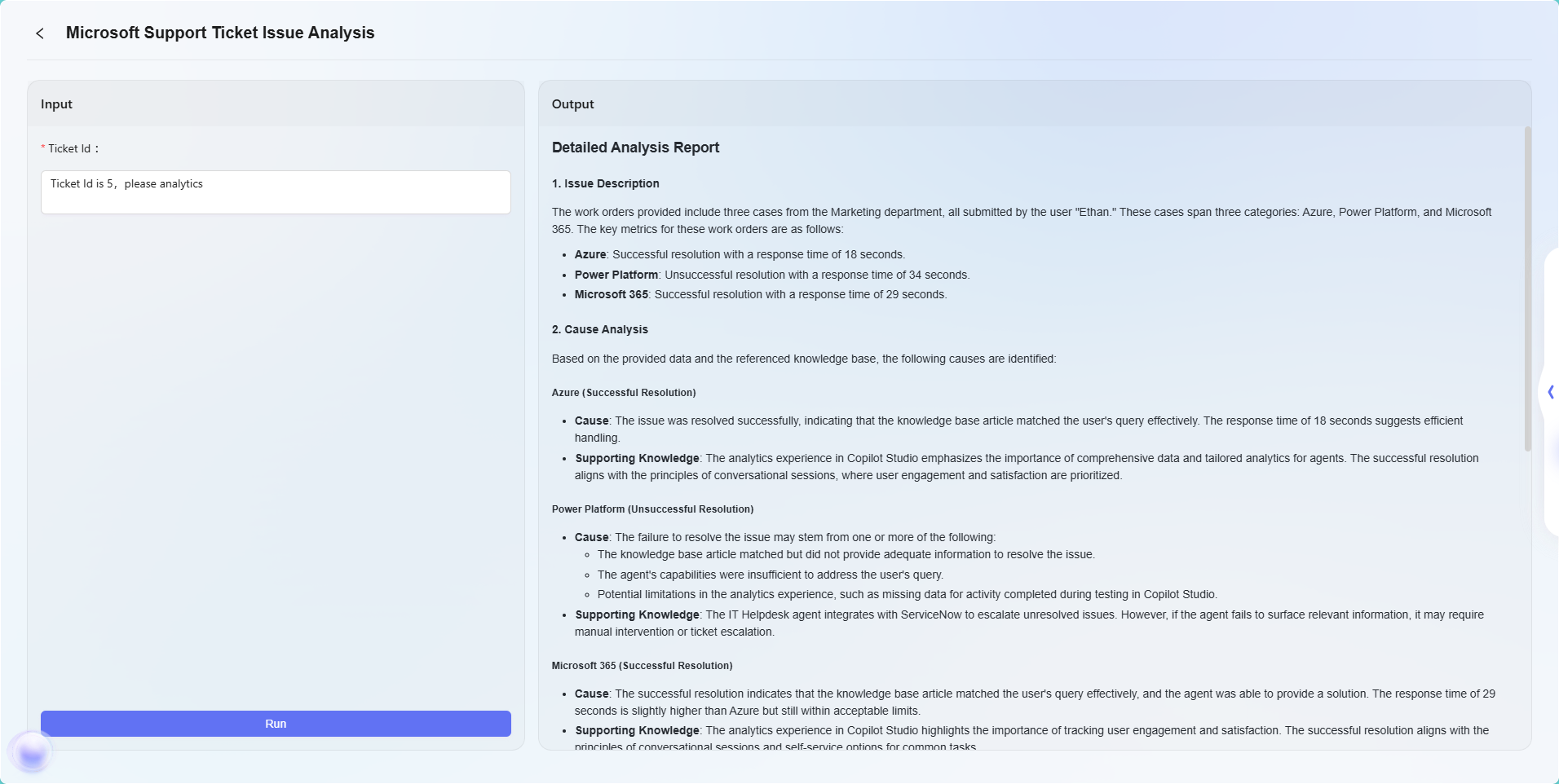
Note: This example is only a simple application of the advanced orchestration feature, used to demonstrate its basic workflow effect. Advanced orchestration has powerful flexibility and scalability, supporting the implementation of complex business logic and intelligent automation processes through various node types, and can be widely applied in a variety of real-world business scenarios.